diff --git a/docs/notes/设计模式 - 单例.md b/docs/notes/设计模式 - 单例.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..136b0f0e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/notes/设计模式 - 单例.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
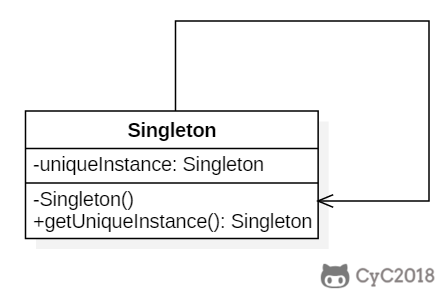
+## 单例(Singleton)
+
+### Intent
+
+确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供该实例的全局访问点。
+
+### Class Diagram
+
+使用一个私有构造函数、一个私有静态变量以及一个公有静态函数来实现。
+
+私有构造函数保证了不能通过构造函数来创建对象实例,只能通过公有静态函数返回唯一的私有静态变量。
+
+
+
+### Implementation
+
+#### Ⅰ 懒汉式-线程不安全
+
+以下实现中,私有静态变量 uniqueInstance 被延迟实例化,这样做的好处是,如果没有用到该类,那么就不会实例化 uniqueInstance,从而节约资源。
+
+这个实现在多线程环境下是不安全的,如果多个线程能够同时进入 `if (uniqueInstance == null)` ,并且此时 uniqueInstance 为 null,那么会有多个线程执行 `uniqueInstance = new Singleton();` 语句,这将导致实例化多次 uniqueInstance。
+
+```java
+public class Singleton {
+
+ private static Singleton uniqueInstance;
+
+ private Singleton() {
+ }
+
+ public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+ return uniqueInstance;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### Ⅱ 饿汉式-线程安全
+
+线程不安全问题主要是由于 uniqueInstance 被实例化多次,采取直接实例化 uniqueInstance 的方式就不会产生线程不安全问题。
+
+但是直接实例化的方式也丢失了延迟实例化带来的节约资源的好处。
+
+```java
+private static Singleton uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+```
+
+#### Ⅲ 懒汉式-线程安全
+
+只需要对 getUniqueInstance() 方法加锁,那么在一个时间点只能有一个线程能够进入该方法,从而避免了实例化多次 uniqueInstance。
+
+但是当一个线程进入该方法之后,其它试图进入该方法的线程都必须等待,即使 uniqueInstance 已经被实例化了。这会让线程阻塞时间过长,因此该方法有性能问题,不推荐使用。
+
+```java
+public static synchronized Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+ return uniqueInstance;
+}
+```
+
+#### Ⅳ 双重校验锁-线程安全
+
+uniqueInstance 只需要被实例化一次,之后就可以直接使用了。加锁操作只需要对实例化那部分的代码进行,只有当 uniqueInstance 没有被实例化时,才需要进行加锁。
+
+双重校验锁先判断 uniqueInstance 是否已经被实例化,如果没有被实例化,那么才对实例化语句进行加锁。
+
+```java
+public class Singleton {
+
+ private volatile static Singleton uniqueInstance;
+
+ private Singleton() {
+ }
+
+ public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ synchronized (Singleton.class) {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return uniqueInstance;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+考虑下面的实现,也就是只使用了一个 if 语句。在 uniqueInstance == null 的情况下,如果两个线程都执行了 if 语句,那么两个线程都会进入 if 语句块内。虽然在 if 语句块内有加锁操作,但是两个线程都会执行 `uniqueInstance = new Singleton();` 这条语句,只是先后的问题,那么就会进行两次实例化。因此必须使用双重校验锁,也就是需要使用两个 if 语句:第一个 if 语句用来避免 uniqueInstance 已经被实例化之后的加锁操作,而第二个 if 语句进行了加锁,所以只能有一个线程进入,就不会出现 uniqueInstance == null 时两个线程同时进行实例化操作。
+
+```java
+if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ synchronized (Singleton.class) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+uniqueInstance 采用 volatile 关键字修饰也是很有必要的, `uniqueInstance = new Singleton();` 这段代码其实是分为三步执行:
+
+1. 为 uniqueInstance 分配内存空间
+2. 初始化 uniqueInstance
+3. 将 uniqueInstance 指向分配的内存地址
+
+但是由于 JVM 具有指令重排的特性,执行顺序有可能变成 1>3>2。指令重排在单线程环境下不会出现问题,但是在多线程环境下会导致一个线程获得还没有初始化的实例。例如,线程 T1 执行了 1 和 3,此时 T2 调用 getUniqueInstance() 后发现 uniqueInstance 不为空,因此返回 uniqueInstance,但此时 uniqueInstance 还未被初始化。
+
+使用 volatile 可以禁止 JVM 的指令重排,保证在多线程环境下也能正常运行。
+
+#### Ⅴ 静态内部类实现
+
+当 Singleton 类被加载时,静态内部类 SingletonHolder 没有被加载进内存。只有当调用 `getUniqueInstance()` 方法从而触发 `SingletonHolder.INSTANCE` 时 SingletonHolder 才会被加载,此时初始化 INSTANCE 实例,并且 JVM 能确保 INSTANCE 只被实例化一次。
+
+这种方式不仅具有延迟初始化的好处,而且由 JVM 提供了对线程安全的支持。
+
+```java
+public class Singleton {
+
+ private Singleton() {
+ }
+
+ private static class SingletonHolder {
+ private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
+ }
+
+ public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### Ⅵ 枚举实现
+
+```java
+public enum Singleton {
+
+ INSTANCE;
+
+ private String objName;
+
+
+ public String getObjName() {
+ return objName;
+ }
+
+
+ public void setObjName(String objName) {
+ this.objName = objName;
+ }
+
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+
+ // 单例测试
+ Singleton firstSingleton = Singleton.INSTANCE;
+ firstSingleton.setObjName("firstName");
+ System.out.println(firstSingleton.getObjName());
+ Singleton secondSingleton = Singleton.INSTANCE;
+ secondSingleton.setObjName("secondName");
+ System.out.println(firstSingleton.getObjName());
+ System.out.println(secondSingleton.getObjName());
+
+ // 反射获取实例测试
+ try {
+ Singleton[] enumConstants = Singleton.class.getEnumConstants();
+ for (Singleton enumConstant : enumConstants) {
+ System.out.println(enumConstant.getObjName());
+ }
+ } catch (Exception e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+firstName
+secondName
+secondName
+secondName
+```
+
+该实现可以防止反射攻击。在其它实现中,通过 setAccessible() 方法可以将私有构造函数的访问级别设置为 public,然后调用构造函数从而实例化对象,如果要防止这种攻击,需要在构造函数中添加防止多次实例化的代码。该实现是由 JVM 保证只会实例化一次,因此不会出现上述的反射攻击。
+
+该实现在多次序列化和序列化之后,不会得到多个实例。而其它实现需要使用 transient 修饰所有字段,并且实现序列化和反序列化的方法。
+
+### Examples
+
+- Logger Classes
+- Configuration Classes
+- Accesing resources in shared mode
+- Factories implemented as Singletons
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.Runtime#getRuntime()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Runtime.html#getRuntime%28%29)
+- [java.awt.Desktop#getDesktop()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/awt/Desktop.html#getDesktop--)
+- [java.lang.System#getSecurityManager()](
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
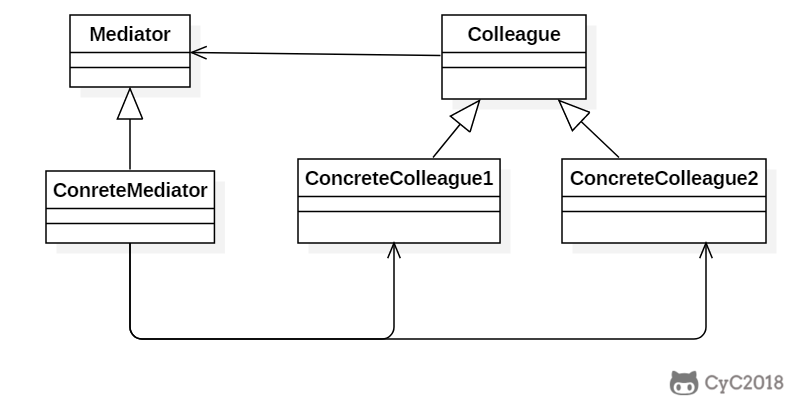
+### Implementation
+
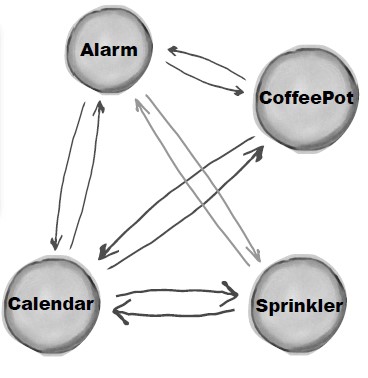
+Alarm(闹钟)、CoffeePot(咖啡壶)、Calendar(日历)、Sprinkler(喷头)是一组相关的对象,在某个对象的事件产生时需要去操作其它对象,形成了下面这种依赖结构:
+
+ 
+
+使用中介者模式可以将复杂的依赖结构变成星形结构:
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public abstract class Colleague {
+ public abstract void onEvent(Mediator mediator);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Alarm extends Colleague {
+
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("alarm");
+ }
+
+ public void doAlarm() {
+ System.out.println("doAlarm()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class CoffeePot extends Colleague {
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("coffeePot");
+ }
+
+ public void doCoffeePot() {
+ System.out.println("doCoffeePot()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Calender extends Colleague {
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("calender");
+ }
+
+ public void doCalender() {
+ System.out.println("doCalender()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Sprinkler extends Colleague {
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("sprinkler");
+ }
+
+ public void doSprinkler() {
+ System.out.println("doSprinkler()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class Mediator {
+ public abstract void doEvent(String eventType);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteMediator extends Mediator {
+ private Alarm alarm;
+ private CoffeePot coffeePot;
+ private Calender calender;
+ private Sprinkler sprinkler;
+
+ public ConcreteMediator(Alarm alarm, CoffeePot coffeePot, Calender calender, Sprinkler sprinkler) {
+ this.alarm = alarm;
+ this.coffeePot = coffeePot;
+ this.calender = calender;
+ this.sprinkler = sprinkler;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void doEvent(String eventType) {
+ switch (eventType) {
+ case "alarm":
+ doAlarmEvent();
+ break;
+ case "coffeePot":
+ doCoffeePotEvent();
+ break;
+ case "calender":
+ doCalenderEvent();
+ break;
+ default:
+ doSprinklerEvent();
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void doAlarmEvent() {
+ alarm.doAlarm();
+ coffeePot.doCoffeePot();
+ calender.doCalender();
+ sprinkler.doSprinkler();
+ }
+
+ public void doCoffeePotEvent() {
+ // ...
+ }
+
+ public void doCalenderEvent() {
+ // ...
+ }
+
+ public void doSprinklerEvent() {
+ // ...
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Alarm alarm = new Alarm();
+ CoffeePot coffeePot = new CoffeePot();
+ Calender calender = new Calender();
+ Sprinkler sprinkler = new Sprinkler();
+ Mediator mediator = new ConcreteMediator(alarm, coffeePot, calender, sprinkler);
+ // 闹钟事件到达,调用中介者就可以操作相关对象
+ alarm.onEvent(mediator);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+doAlarm()
+doCoffeePot()
+doCalender()
+doSprinkler()
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- All scheduleXXX() methods of [java.util.Timer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Timer.html)
+- [java.util.concurrent.Executor#execute()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/Executor.html#execute-java.lang.Runnable-)
+- submit() and invokeXXX() methods of [java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/ExecutorService.html)
+- scheduleXXX() methods of [java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/ScheduledExecutorService.html)
+- [java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/reflect/Method.html#invoke-java.lang.Object-java.lang.Object...-)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
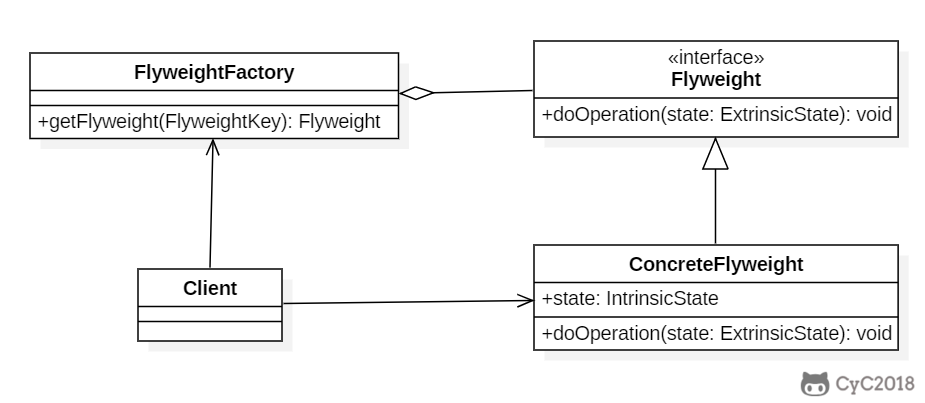
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Flyweight {
+ void doOperation(String extrinsicState);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFlyweight implements Flyweight {
+
+ private String intrinsicState;
+
+ public ConcreteFlyweight(String intrinsicState) {
+ this.intrinsicState = intrinsicState;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void doOperation(String extrinsicState) {
+ System.out.println("Object address: " + System.identityHashCode(this));
+ System.out.println("IntrinsicState: " + intrinsicState);
+ System.out.println("ExtrinsicState: " + extrinsicState);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class FlyweightFactory {
+
+ private HashMap flyweights = new HashMap<>();
+
+ Flyweight getFlyweight(String intrinsicState) {
+ if (!flyweights.containsKey(intrinsicState)) {
+ Flyweight flyweight = new ConcreteFlyweight(intrinsicState);
+ flyweights.put(intrinsicState, flyweight);
+ }
+ return flyweights.get(intrinsicState);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory();
+ Flyweight flyweight1 = factory.getFlyweight("aa");
+ Flyweight flyweight2 = factory.getFlyweight("aa");
+ flyweight1.doOperation("x");
+ flyweight2.doOperation("y");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+Object address: 1163157884
+IntrinsicState: aa
+ExtrinsicState: x
+Object address: 1163157884
+IntrinsicState: aa
+ExtrinsicState: y
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+Java 利用缓存来加速大量小对象的访问时间。
+
+- java.lang.Integer#valueOf(int)
+- java.lang.Boolean#valueOf(boolean)
+- java.lang.Byte#valueOf(byte)
+- java.lang.Character#valueOf(char)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
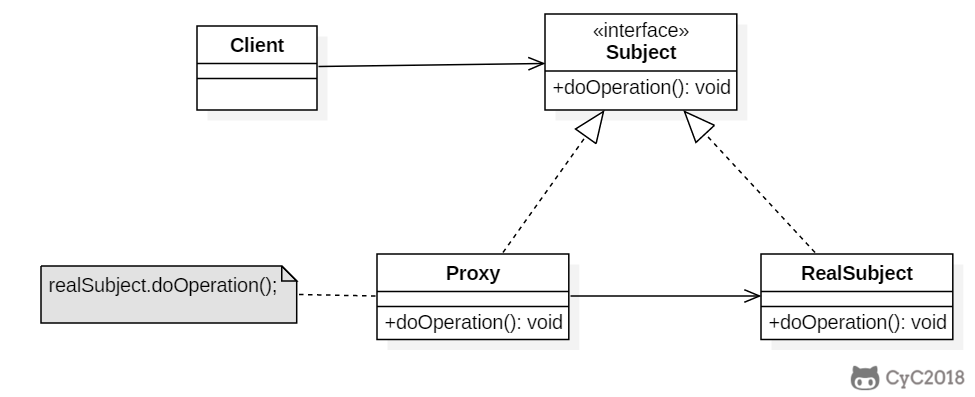
+
+### Implementation
+
+以下是一个虚拟代理的实现,模拟了图片延迟加载的情况下使用与图片大小相等的临时内容去替换原始图片,直到图片加载完成才将图片显示出来。
+
+```java
+public interface Image {
+ void showImage();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class HighResolutionImage implements Image {
+
+ private URL imageURL;
+ private long startTime;
+ private int height;
+ private int width;
+
+ public int getHeight() {
+ return height;
+ }
+
+ public int getWidth() {
+ return width;
+ }
+
+ public HighResolutionImage(URL imageURL) {
+ this.imageURL = imageURL;
+ this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
+ this.width = 600;
+ this.height = 600;
+ }
+
+ public boolean isLoad() {
+ // 模拟图片加载,延迟 3s 加载完成
+ long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
+ return endTime - startTime > 3000;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void showImage() {
+ System.out.println("Real Image: " + imageURL);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ImageProxy implements Image {
+
+ private HighResolutionImage highResolutionImage;
+
+ public ImageProxy(HighResolutionImage highResolutionImage) {
+ this.highResolutionImage = highResolutionImage;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void showImage() {
+ while (!highResolutionImage.isLoad()) {
+ try {
+ System.out.println("Temp Image: " + highResolutionImage.getWidth() + " " + highResolutionImage.getHeight());
+ Thread.sleep(100);
+ } catch (InterruptedException e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ }
+ highResolutionImage.showImage();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ImageViewer {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ String image = "http://image.jpg";
+ URL url = new URL(image);
+ HighResolutionImage highResolutionImage = new HighResolutionImage(url);
+ ImageProxy imageProxy = new ImageProxy(highResolutionImage);
+ imageProxy.showImage();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.lang.reflect.Proxy
+- RMI
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
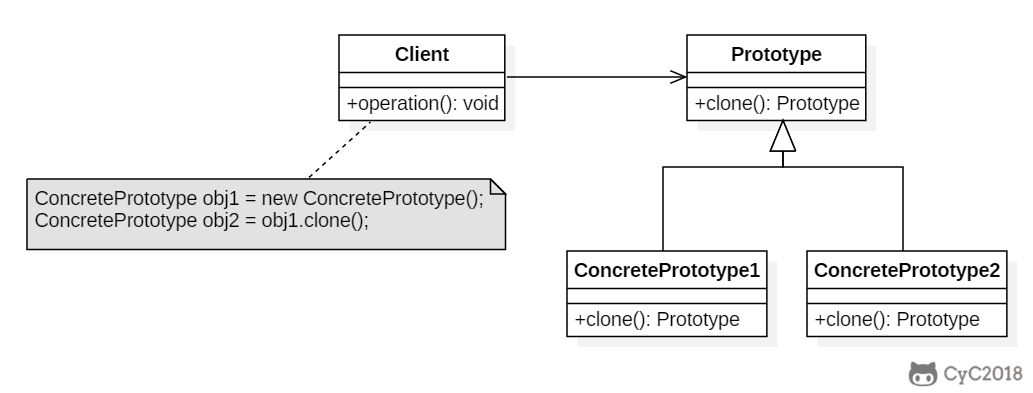
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class Prototype {
+ abstract Prototype myClone();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcretePrototype extends Prototype {
+
+ private String filed;
+
+ public ConcretePrototype(String filed) {
+ this.filed = filed;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ Prototype myClone() {
+ return new ConcretePrototype(filed);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public String toString() {
+ return filed;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Prototype prototype = new ConcretePrototype("abc");
+ Prototype clone = prototype.myClone();
+ System.out.println(clone.toString());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+abc
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.Object#clone()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Object.html#clone%28%29)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
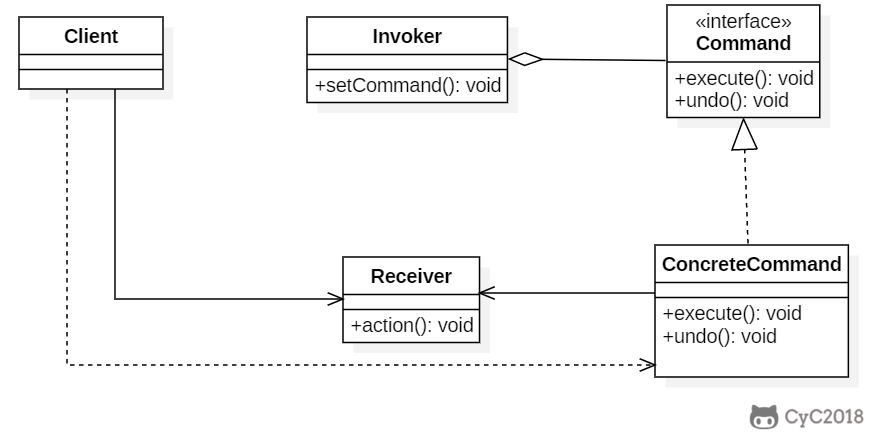
+
+### Implementation
+
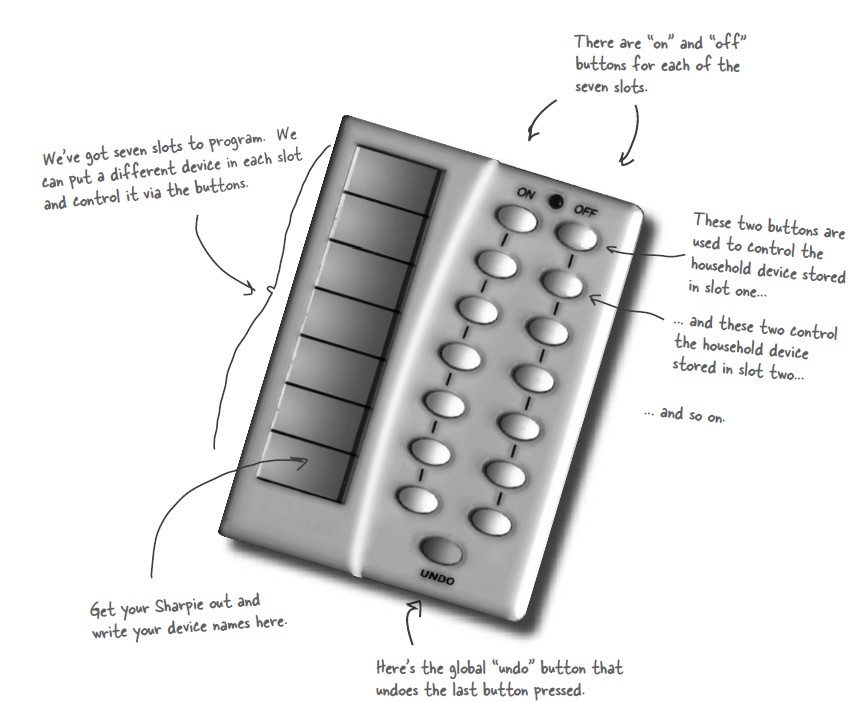
+设计一个遥控器,可以控制电灯开关。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface Command {
+ void execute();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class LightOnCommand implements Command {
+ Light light;
+
+ public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
+ this.light = light;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void execute() {
+ light.on();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class LightOffCommand implements Command {
+ Light light;
+
+ public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
+ this.light = light;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void execute() {
+ light.off();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Light {
+
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("Light is on!");
+ }
+
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("Light is off!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * 遥控器
+ */
+public class Invoker {
+ private Command[] onCommands;
+ private Command[] offCommands;
+ private final int slotNum = 7;
+
+ public Invoker() {
+ this.onCommands = new Command[slotNum];
+ this.offCommands = new Command[slotNum];
+ }
+
+ public void setOnCommand(Command command, int slot) {
+ onCommands[slot] = command;
+ }
+
+ public void setOffCommand(Command command, int slot) {
+ offCommands[slot] = command;
+ }
+
+ public void onButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
+ onCommands[slot].execute();
+ }
+
+ public void offButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
+ offCommands[slot].execute();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Invoker invoker = new Invoker();
+ Light light = new Light();
+ Command lightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(light);
+ Command lightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(light);
+ invoker.setOnCommand(lightOnCommand, 0);
+ invoker.setOffCommand(lightOffCommand, 0);
+ invoker.onButtonWasPushed(0);
+ invoker.offButtonWasPushed(0);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.Runnable](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Runnable.html)
+- [Netflix Hystrix](https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki)
+- [javax.swing.Action](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/swing/Action.html)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Implementation
+
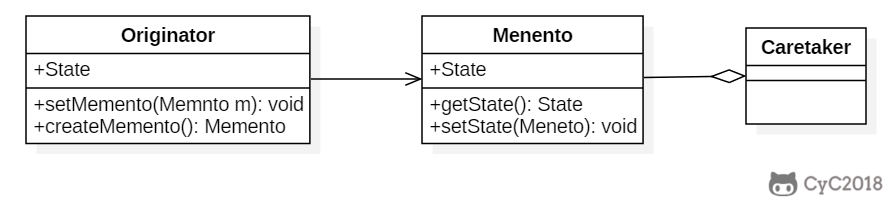
+以下实现了一个简单计算器程序,可以输入两个值,然后计算这两个值的和。备忘录模式允许将这两个值存储起来,然后在某个时刻用存储的状态进行恢复。
+
+实现参考:[Memento Pattern - Calculator Example - Java Sourcecode](https://www.oodesign.com/memento-pattern-calculator-example-java-sourcecode.html)
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Originator Interface
+ */
+public interface Calculator {
+
+ // Create Memento
+ PreviousCalculationToCareTaker backupLastCalculation();
+
+ // setMemento
+ void restorePreviousCalculation(PreviousCalculationToCareTaker memento);
+
+ int getCalculationResult();
+
+ void setFirstNumber(int firstNumber);
+
+ void setSecondNumber(int secondNumber);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Originator Implementation
+ */
+public class CalculatorImp implements Calculator {
+
+ private int firstNumber;
+ private int secondNumber;
+
+ @Override
+ public PreviousCalculationToCareTaker backupLastCalculation() {
+ // create a memento object used for restoring two numbers
+ return new PreviousCalculationImp(firstNumber, secondNumber);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void restorePreviousCalculation(PreviousCalculationToCareTaker memento) {
+ this.firstNumber = ((PreviousCalculationToOriginator) memento).getFirstNumber();
+ this.secondNumber = ((PreviousCalculationToOriginator) memento).getSecondNumber();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int getCalculationResult() {
+ // result is adding two numbers
+ return firstNumber + secondNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void setFirstNumber(int firstNumber) {
+ this.firstNumber = firstNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void setSecondNumber(int secondNumber) {
+ this.secondNumber = secondNumber;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Memento Interface to Originator
+ *
+ * This interface allows the originator to restore its state
+ */
+public interface PreviousCalculationToOriginator {
+ int getFirstNumber();
+ int getSecondNumber();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Memento interface to CalculatorOperator (Caretaker)
+ */
+public interface PreviousCalculationToCareTaker {
+ // no operations permitted for the caretaker
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Memento Object Implementation
+ *
+ * Note that this object implements both interfaces to Originator and CareTaker
+ */
+public class PreviousCalculationImp implements PreviousCalculationToCareTaker,
+ PreviousCalculationToOriginator {
+
+ private int firstNumber;
+ private int secondNumber;
+
+ public PreviousCalculationImp(int firstNumber, int secondNumber) {
+ this.firstNumber = firstNumber;
+ this.secondNumber = secondNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int getFirstNumber() {
+ return firstNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int getSecondNumber() {
+ return secondNumber;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * CareTaker object
+ */
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ // program starts
+ Calculator calculator = new CalculatorImp();
+
+ // assume user enters two numbers
+ calculator.setFirstNumber(10);
+ calculator.setSecondNumber(100);
+
+ // find result
+ System.out.println(calculator.getCalculationResult());
+
+ // Store result of this calculation in case of error
+ PreviousCalculationToCareTaker memento = calculator.backupLastCalculation();
+
+ // user enters a number
+ calculator.setFirstNumber(17);
+
+ // user enters a wrong second number and calculates result
+ calculator.setSecondNumber(-290);
+
+ // calculate result
+ System.out.println(calculator.getCalculationResult());
+
+ // user hits CTRL + Z to undo last operation and see last result
+ calculator.restorePreviousCalculation(memento);
+
+ // result restored
+ System.out.println(calculator.getCalculationResult());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+110
+-273
+110
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.io.Serializable
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
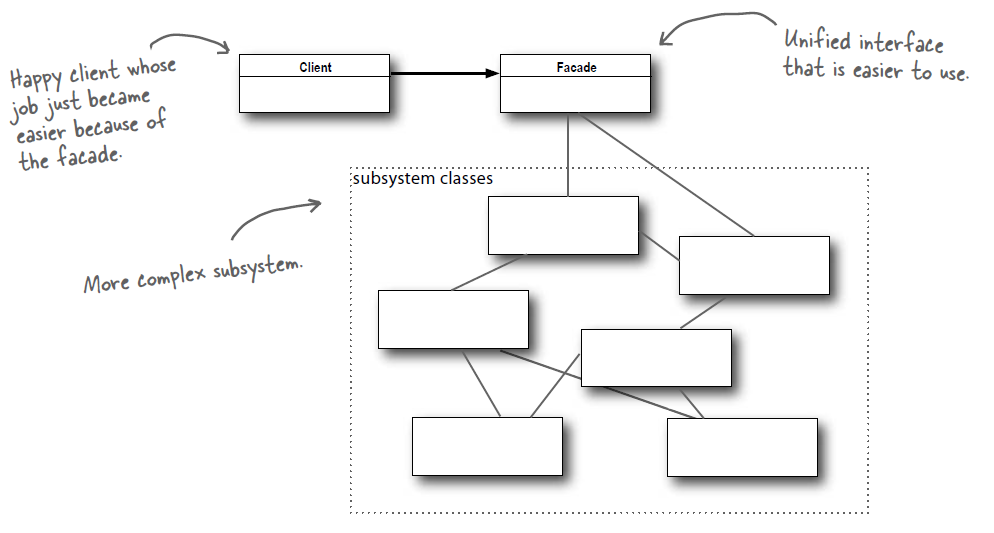
+观看电影需要操作很多电器,使用外观模式实现一键看电影功能。
+
+```java
+public class SubSystem {
+ public void turnOnTV() {
+ System.out.println("turnOnTV()");
+ }
+
+ public void setCD(String cd) {
+ System.out.println("setCD( " + cd + " )");
+ }
+
+ public void startWatching(){
+ System.out.println("startWatching()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Facade {
+ private SubSystem subSystem = new SubSystem();
+
+ public void watchMovie() {
+ subSystem.turnOnTV();
+ subSystem.setCD("a movie");
+ subSystem.startWatching();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Facade facade = new Facade();
+ facade.watchMovie();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### 设计原则
+
+最少知识原则:只和你的密友谈话。也就是说客户对象所需要交互的对象应当尽可能少。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
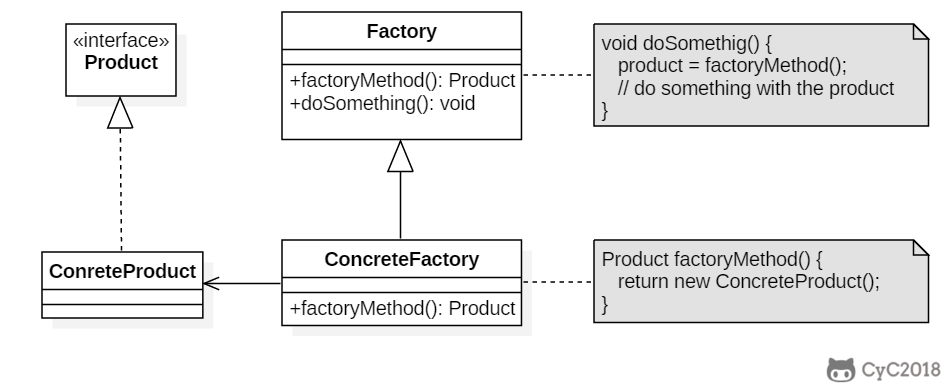
+public abstract class Factory {
+ abstract public Product factoryMethod();
+ public void doSomething() {
+ Product product = factoryMethod();
+ // do something with the product
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory extends Factory {
+ public Product factoryMethod() {
+ return new ConcreteProduct();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory1 extends Factory {
+ public Product factoryMethod() {
+ return new ConcreteProduct1();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory2 extends Factory {
+ public Product factoryMethod() {
+ return new ConcreteProduct2();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Calendar](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Calendar.html#getInstance--)
+- [java.util.ResourceBundle](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/ResourceBundle.html#getBundle-java.lang.String-)
+- [java.text.NumberFormat](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/text/NumberFormat.html#getInstance--)
+- [java.nio.charset.Charset](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/charset/Charset.html#forName-java.lang.String-)
+- [java.net.URLStreamHandlerFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/net/URLStreamHandlerFactory.html#createURLStreamHandler-java.lang.String-)
+- [java.util.EnumSet](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/EnumSet.html#of-E-)
+- [javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/bind/JAXBContext.html#createMarshaller--)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
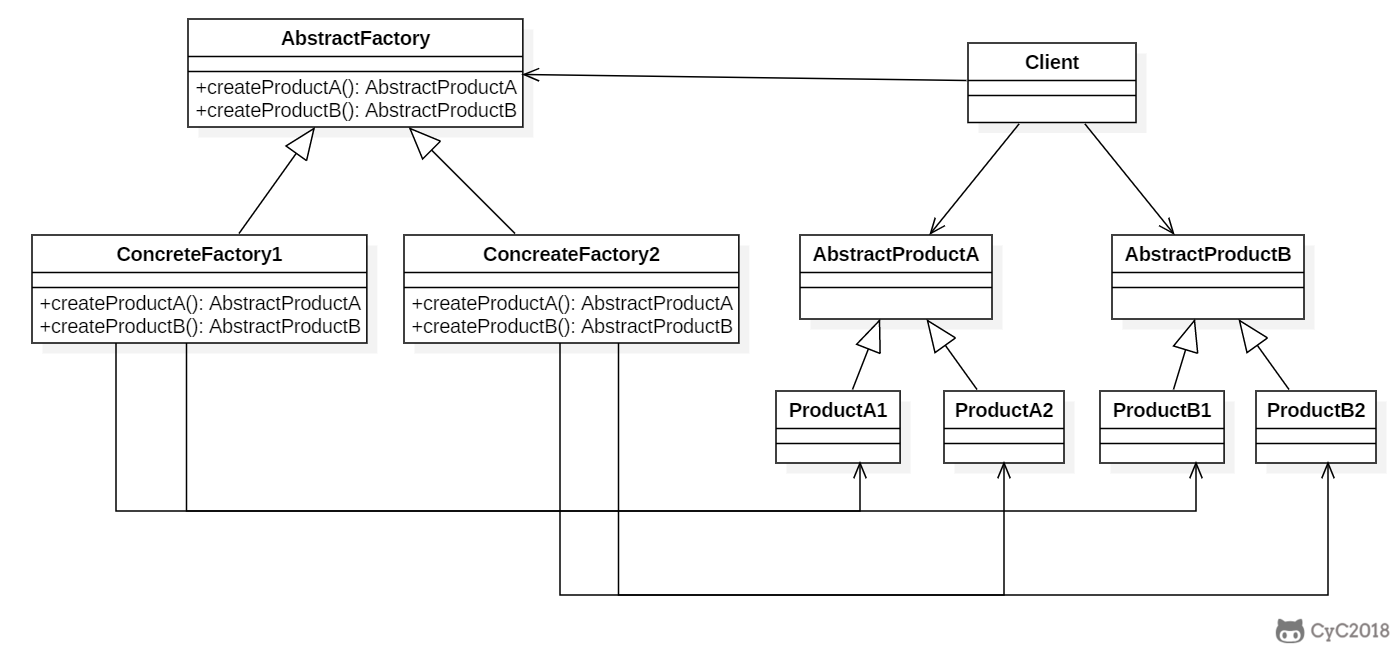
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public class AbstractProductA {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class AbstractProductB {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductA1 extends AbstractProductA {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductA2 extends AbstractProductA {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductB1 extends AbstractProductB {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductB2 extends AbstractProductB {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class AbstractFactory {
+ abstract AbstractProductA createProductA();
+ abstract AbstractProductB createProductB();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory1 extends AbstractFactory {
+ AbstractProductA createProductA() {
+ return new ProductA1();
+ }
+
+ AbstractProductB createProductB() {
+ return new ProductB1();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory2 extends AbstractFactory {
+ AbstractProductA createProductA() {
+ return new ProductA2();
+ }
+
+ AbstractProductB createProductB() {
+ return new ProductB2();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ AbstractFactory abstractFactory = new ConcreteFactory1();
+ AbstractProductA productA = abstractFactory.createProductA();
+ AbstractProductB productB = abstractFactory.createProductB();
+ // do something with productA and productB
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/parsers/DocumentBuilderFactory.html)
+- [javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/transform/TransformerFactory.html#newInstance--)
+- [javax.xml.xpath.XPathFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/xpath/XPathFactory.html#newInstance--)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
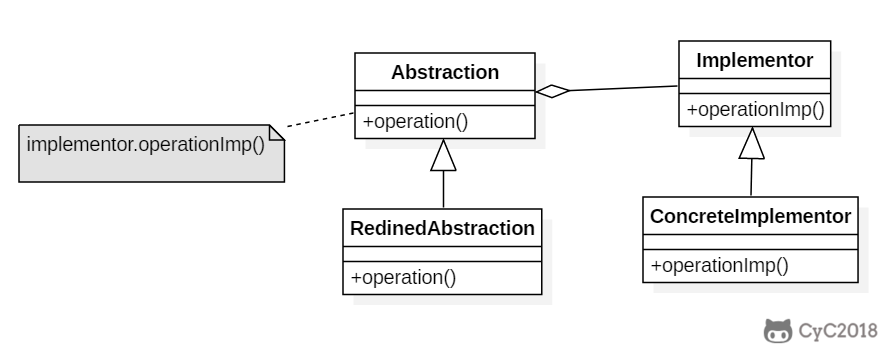
+
+### Implementation
+
+RemoteControl 表示遥控器,指代 Abstraction。
+
+TV 表示电视,指代 Implementor。
+
+桥接模式将遥控器和电视分离开来,从而可以独立改变遥控器或者电视的实现。
+
+```java
+public abstract class TV {
+ public abstract void on();
+
+ public abstract void off();
+
+ public abstract void tuneChannel();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Sony extends TV {
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("Sony.on()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("Sony.off()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("Sony.tuneChannel()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class RCA extends TV {
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("RCA.on()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("RCA.off()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("RCA.tuneChannel()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class RemoteControl {
+ protected TV tv;
+
+ public RemoteControl(TV tv) {
+ this.tv = tv;
+ }
+
+ public abstract void on();
+
+ public abstract void off();
+
+ public abstract void tuneChannel();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteRemoteControl1 extends RemoteControl {
+ public ConcreteRemoteControl1(TV tv) {
+ super(tv);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl1.on()");
+ tv.on();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl1.off()");
+ tv.off();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl1.tuneChannel()");
+ tv.tuneChannel();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteRemoteControl2 extends RemoteControl {
+ public ConcreteRemoteControl2(TV tv) {
+ super(tv);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl2.on()");
+ tv.on();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl2.off()");
+ tv.off();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl2.tuneChannel()");
+ tv.tuneChannel();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ RemoteControl remoteControl1 = new ConcreteRemoteControl1(new RCA());
+ remoteControl1.on();
+ remoteControl1.off();
+ remoteControl1.tuneChannel();
+ RemoteControl remoteControl2 = new ConcreteRemoteControl2(new Sony());
+ remoteControl2.on();
+ remoteControl2.off();
+ remoteControl2.tuneChannel();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- AWT (It provides an abstraction layer which maps onto the native OS the windowing support.)
+- JDBC
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
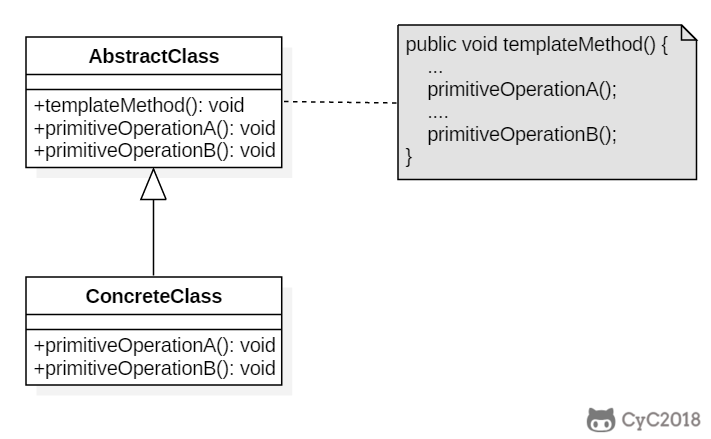
+
+### Implementation
+
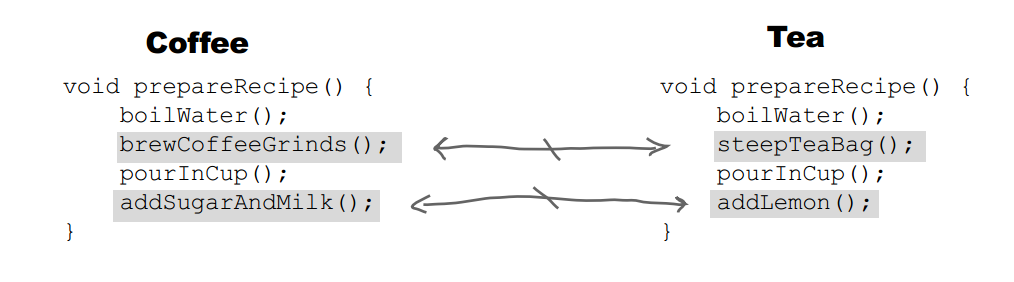
+冲咖啡和冲茶都有类似的流程,但是某些步骤会有点不一样,要求复用那些相同步骤的代码。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public abstract class CaffeineBeverage {
+
+ final void prepareRecipe() {
+ boilWater();
+ brew();
+ pourInCup();
+ addCondiments();
+ }
+
+ abstract void brew();
+
+ abstract void addCondiments();
+
+ void boilWater() {
+ System.out.println("boilWater");
+ }
+
+ void pourInCup() {
+ System.out.println("pourInCup");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Coffee extends CaffeineBeverage {
+ @Override
+ void brew() {
+ System.out.println("Coffee.brew");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void addCondiments() {
+ System.out.println("Coffee.addCondiments");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Tea extends CaffeineBeverage {
+ @Override
+ void brew() {
+ System.out.println("Tea.brew");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void addCondiments() {
+ System.out.println("Tea.addCondiments");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ CaffeineBeverage caffeineBeverage = new Coffee();
+ caffeineBeverage.prepareRecipe();
+ System.out.println("-----------");
+ caffeineBeverage = new Tea();
+ caffeineBeverage.prepareRecipe();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+boilWater
+Coffee.brew
+pourInCup
+Coffee.addCondiments
+-----------
+boilWater
+Tea.brew
+pourInCup
+Tea.addCondiments
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.util.Collections#sort()
+- java.io.InputStream#skip()
+- java.io.InputStream#read()
+- java.util.AbstractList#indexOf()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
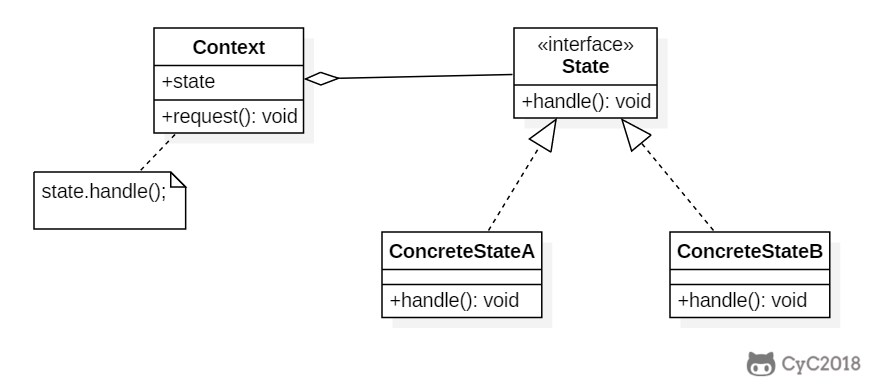
+
+### Implementation
+
+糖果销售机有多种状态,每种状态下销售机有不同的行为,状态可以发生转移,使得销售机的行为也发生改变。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface State {
+ /**
+ * 投入 25 分钱
+ */
+ void insertQuarter();
+
+ /**
+ * 退回 25 分钱
+ */
+ void ejectQuarter();
+
+ /**
+ * 转动曲柄
+ */
+ void turnCrank();
+
+ /**
+ * 发放糖果
+ */
+ void dispense();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class HasQuarterState implements State {
+
+ private GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You can't insert another quarter");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("Quarter returned");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("You turned...");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldState());
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class NoQuarterState implements State {
+
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You insert a quarter");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getHasQuarterState());
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You haven't insert a quarter");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("You turned, but there's no quarter");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ System.out.println("You need to pay first");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class SoldOutState implements State {
+
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public SoldOutState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You can't eject, you haven't inserted a quarter yet");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("You turned, but there are no gumballs");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class SoldState implements State {
+
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public SoldState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a gumball");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("Sorry, you already turned the crank");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("Turning twice doesn't get you another gumball!");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ gumballMachine.releaseBall();
+ if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
+ } else {
+ System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class GumballMachine {
+
+ private State soldOutState;
+ private State noQuarterState;
+ private State hasQuarterState;
+ private State soldState;
+
+ private State state;
+ private int count = 0;
+
+ public GumballMachine(int numberGumballs) {
+ count = numberGumballs;
+ soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
+ noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
+ hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
+ soldState = new SoldState(this);
+
+ if (numberGumballs > 0) {
+ state = noQuarterState;
+ } else {
+ state = soldOutState;
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ state.insertQuarter();
+ }
+
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ state.ejectQuarter();
+ }
+
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ state.turnCrank();
+ state.dispense();
+ }
+
+ public void setState(State state) {
+ this.state = state;
+ }
+
+ public void releaseBall() {
+ System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot...");
+ if (count != 0) {
+ count -= 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ public State getSoldOutState() {
+ return soldOutState;
+ }
+
+ public State getNoQuarterState() {
+ return noQuarterState;
+ }
+
+ public State getHasQuarterState() {
+ return hasQuarterState;
+ }
+
+ public State getSoldState() {
+ return soldState;
+ }
+
+ public int getCount() {
+ return count;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine = new GumballMachine(5);
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.ejectQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.ejectQuarter();
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You insert a quarter
+Quarter returned
+You turned, but there's no quarter
+You need to pay first
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You haven't insert a quarter
+You insert a quarter
+You can't insert another quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+Oops, out of gumballs
+You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out
+You turned, but there are no gumballs
+No gumball dispensed
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
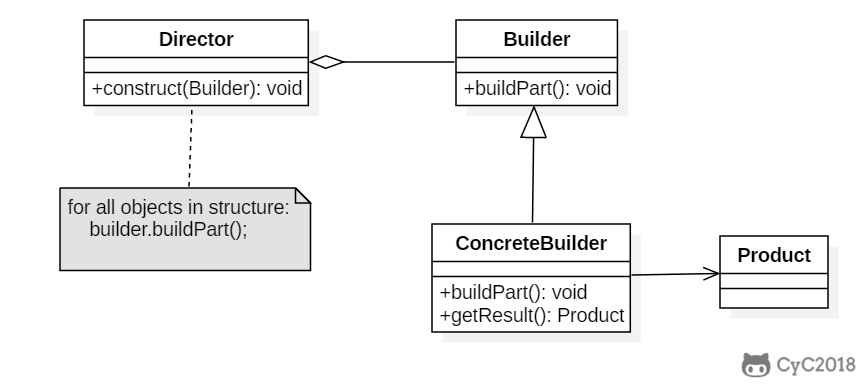
+
+### Implementation
+
+以下是一个简易的 StringBuilder 实现,参考了 JDK 1.8 源码。
+
+```java
+public class AbstractStringBuilder {
+ protected char[] value;
+
+ protected int count;
+
+ public AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
+ count = 0;
+ value = new char[capacity];
+ }
+
+ public AbstractStringBuilder append(char c) {
+ ensureCapacityInternal(count + 1);
+ value[count++] = c;
+ return this;
+ }
+
+ private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
+ // overflow-conscious code
+ if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0)
+ expandCapacity(minimumCapacity);
+ }
+
+ void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
+ int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
+ if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
+ newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
+ if (newCapacity < 0) {
+ if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow
+ throw new OutOfMemoryError();
+ newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ }
+ value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class StringBuilder extends AbstractStringBuilder {
+ public StringBuilder() {
+ super(16);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public String toString() {
+ // Create a copy, don't share the array
+ return new String(value, 0, count);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
+ final int count = 26;
+ for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
+ sb.append((char) ('a' + i));
+ }
+ System.out.println(sb.toString());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.StringBuilder](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/StringBuilder.html)
+- [java.nio.ByteBuffer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/ByteBuffer.html#put-byte-)
+- [java.lang.StringBuffer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/StringBuffer.html#append-boolean-)
+- [java.lang.Appendable](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Appendable.html)
+- [Apache Camel builders](https://github.com/apache/camel/tree/0e195428ee04531be27a0b659005e3aa8d159d23/camel-core/src/main/java/org/apache/camel/builder)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+


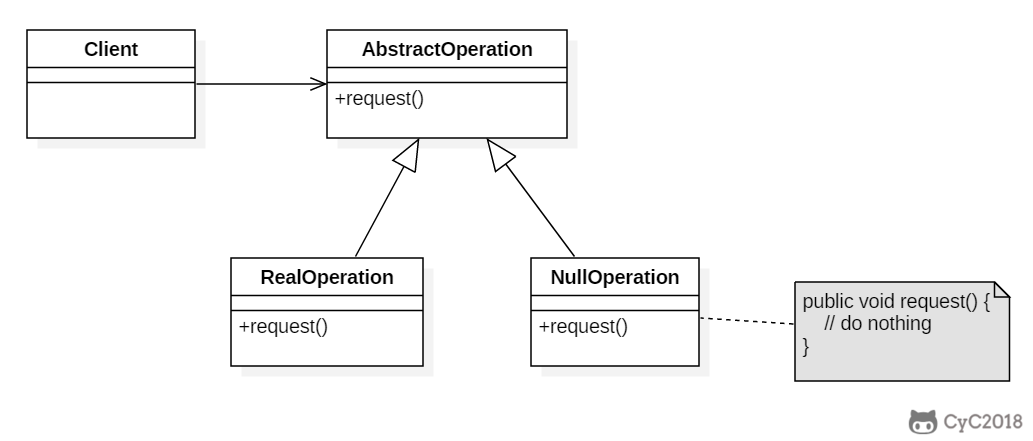
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class AbstractOperation {
+ abstract void request();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class RealOperation extends AbstractOperation {
+ @Override
+ void request() {
+ System.out.println("do something");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class NullOperation extends AbstractOperation{
+ @Override
+ void request() {
+ // do nothing
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ AbstractOperation abstractOperation = func(-1);
+ abstractOperation.request();
+ }
+
+ public static AbstractOperation func(int para) {
+ if (para < 0) {
+ return new NullOperation();
+ }
+ return new RealOperation();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
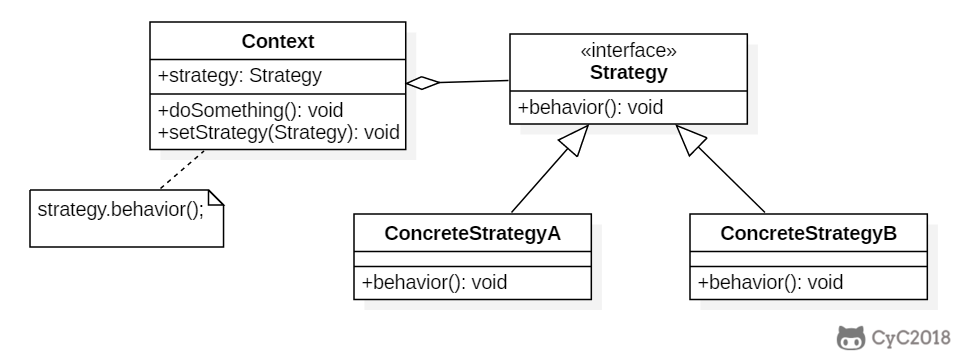
+
+### 与状态模式的比较
+
+状态模式的类图和策略模式类似,并且都是能够动态改变对象的行为。但是状态模式是通过状态转移来改变 Context 所组合的 State 对象,而策略模式是通过 Context 本身的决策来改变组合的 Strategy 对象。所谓的状态转移,是指 Context 在运行过程中由于一些条件发生改变而使得 State 对象发生改变,注意必须要是在运行过程中。
+
+状态模式主要是用来解决状态转移的问题,当状态发生转移了,那么 Context 对象就会改变它的行为;而策略模式主要是用来封装一组可以互相替代的算法族,并且可以根据需要动态地去替换 Context 使用的算法。
+
+### Implementation
+
+设计一个鸭子,它可以动态地改变叫声。这里的算法族是鸭子的叫声行为。
+
+```java
+public interface QuackBehavior {
+ void quack();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Quack implements QuackBehavior {
+ @Override
+ public void quack() {
+ System.out.println("quack!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Squeak implements QuackBehavior{
+ @Override
+ public void quack() {
+ System.out.println("squeak!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Duck {
+
+ private QuackBehavior quackBehavior;
+
+ public void performQuack() {
+ if (quackBehavior != null) {
+ quackBehavior.quack();
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void setQuackBehavior(QuackBehavior quackBehavior) {
+ this.quackBehavior = quackBehavior;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Duck duck = new Duck();
+ duck.setQuackBehavior(new Squeak());
+ duck.performQuack();
+ duck.setQuackBehavior(new Quack());
+ duck.performQuack();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+squeak!
+quack!
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.util.Comparator#compare()
+- javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet
+- javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Product {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteProduct implements Product {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
+}
+```
+
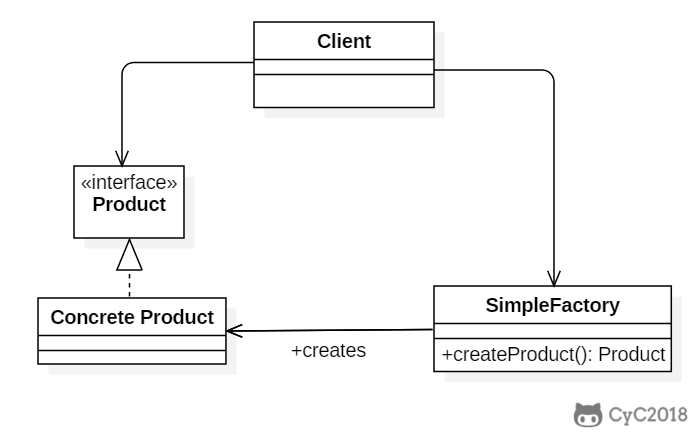
+以下的 Client 类包含了实例化的代码,这是一种错误的实现。如果在客户类中存在这种实例化代码,就需要考虑将代码放到简单工厂中。
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ int type = 1;
+ Product product;
+ if (type == 1) {
+ product = new ConcreteProduct1();
+ } else if (type == 2) {
+ product = new ConcreteProduct2();
+ } else {
+ product = new ConcreteProduct();
+ }
+ // do something with the product
+ }
+}
+```
+
+以下的 SimpleFactory 是简单工厂实现,它被所有需要进行实例化的客户类调用。
+
+```java
+public class SimpleFactory {
+
+ public Product createProduct(int type) {
+ if (type == 1) {
+ return new ConcreteProduct1();
+ } else if (type == 2) {
+ return new ConcreteProduct2();
+ }
+ return new ConcreteProduct();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ SimpleFactory simpleFactory = new SimpleFactory();
+ Product product = simpleFactory.createProduct(1);
+ // do something with the product
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
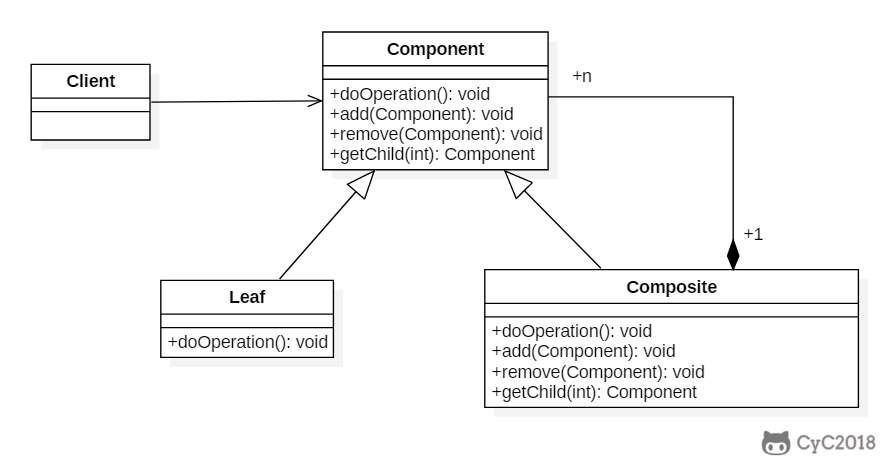
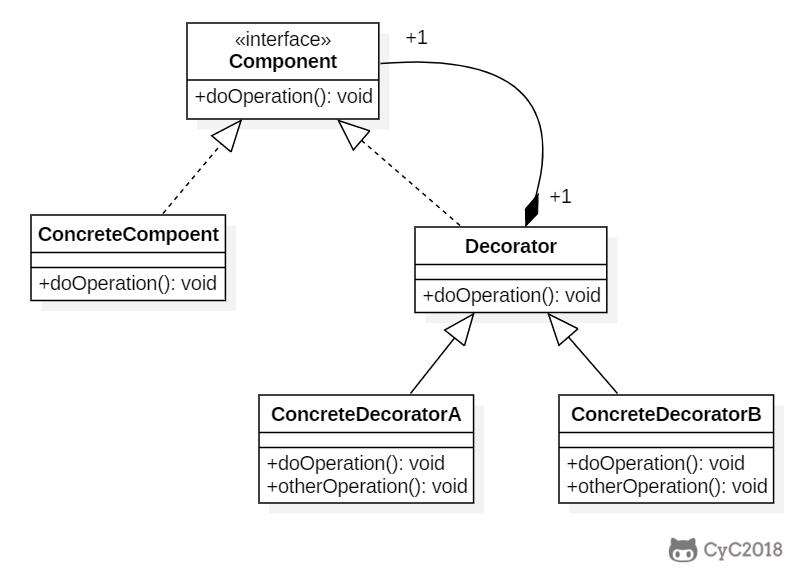
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class Component {
+ protected String name;
+
+ public Component(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ public void print() {
+ print(0);
+ }
+
+ abstract void print(int level);
+
+ abstract public void add(Component component);
+
+ abstract public void remove(Component component);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Composite extends Component {
+
+ private List child;
+
+ public Composite(String name) {
+ super(name);
+ child = new ArrayList<>();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void print(int level) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
+ System.out.print("--");
+ }
+ System.out.println("Composite:" + name);
+ for (Component component : child) {
+ component.print(level + 1);
+ }
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void add(Component component) {
+ child.add(component);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void remove(Component component) {
+ child.remove(component);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Leaf extends Component {
+ public Leaf(String name) {
+ super(name);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void print(int level) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
+ System.out.print("--");
+ }
+ System.out.println("left:" + name);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void add(Component component) {
+ throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); // 牺牲透明性换取单一职责原则,这样就不用考虑是叶子节点还是组合节点
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void remove(Component component) {
+ throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Composite root = new Composite("root");
+ Component node1 = new Leaf("1");
+ Component node2 = new Composite("2");
+ Component node3 = new Leaf("3");
+ root.add(node1);
+ root.add(node2);
+ root.add(node3);
+ Component node21 = new Leaf("21");
+ Component node22 = new Composite("22");
+ node2.add(node21);
+ node2.add(node22);
+ Component node221 = new Leaf("221");
+ node22.add(node221);
+ root.print();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+Composite:root
+--left:1
+--Composite:2
+----left:21
+----Composite:22
+------left:221
+--left:3
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- javax.swing.JComponent#add(Component)
+- java.awt.Container#add(Component)
+- java.util.Map#putAll(Map)
+- java.util.List#addAll(Collection)
+- java.util.Set#addAll(Collection)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Implementation
+
+设计不同种类的饮料,饮料可以添加配料,比如可以添加牛奶,并且支持动态添加新配料。每增加一种配料,该饮料的价格就会增加,要求计算一种饮料的价格。
+
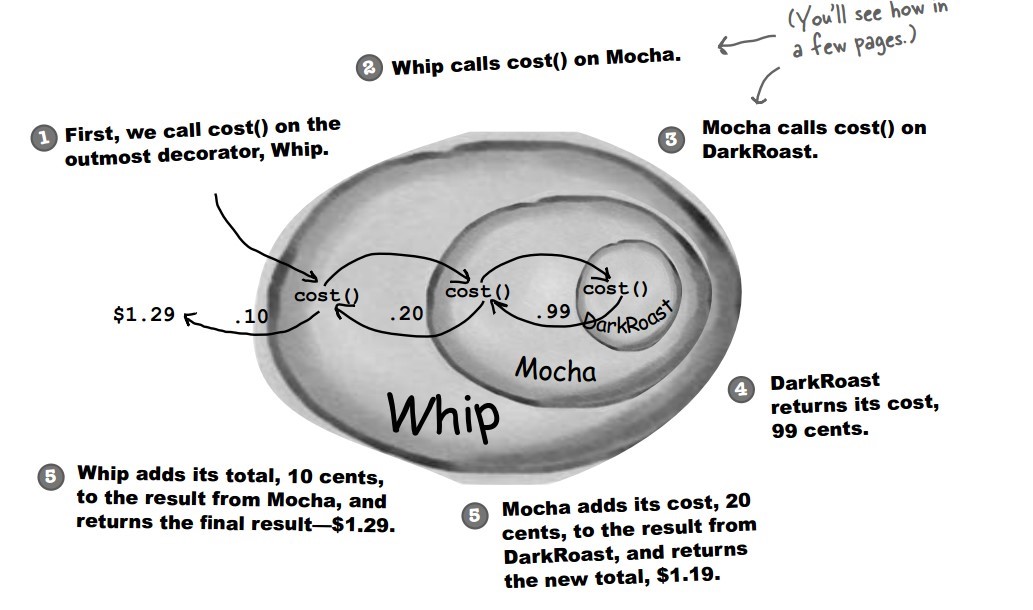
+下图表示在 DarkRoast 饮料上新增新添加 Mocha 配料,之后又添加了 Whip 配料。DarkRoast 被 Mocha 包裹,Mocha 又被 Whip 包裹。它们都继承自相同父类,都有 cost() 方法,外层类的 cost() 方法调用了内层类的 cost() 方法。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface Beverage {
+ double cost();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class DarkRoast implements Beverage {
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class HouseBlend implements Beverage {
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class CondimentDecorator implements Beverage {
+ protected Beverage beverage;
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
+
+ public Milk(Beverage beverage) {
+ this.beverage = beverage;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1 + beverage.cost();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Mocha extends CondimentDecorator {
+
+ public Mocha(Beverage beverage) {
+ this.beverage = beverage;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1 + beverage.cost();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Beverage beverage = new HouseBlend();
+ beverage = new Mocha(beverage);
+ beverage = new Milk(beverage);
+ System.out.println(beverage.cost());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+3.0
+```
+
+### 设计原则
+
+类应该对扩展开放,对修改关闭:也就是添加新功能时不需要修改代码。饮料可以动态添加新的配料,而不需要去修改饮料的代码。
+
+不可能把所有的类设计成都满足这一原则,应当把该原则应用于最有可能发生改变的地方。
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.io.BufferedInputStream(InputStream)
+- java.io.DataInputStream(InputStream)
+- java.io.BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream)
+- java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream(OutputStream)
+- java.util.Collections#checked[List|Map|Set|SortedSet|SortedMap]()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
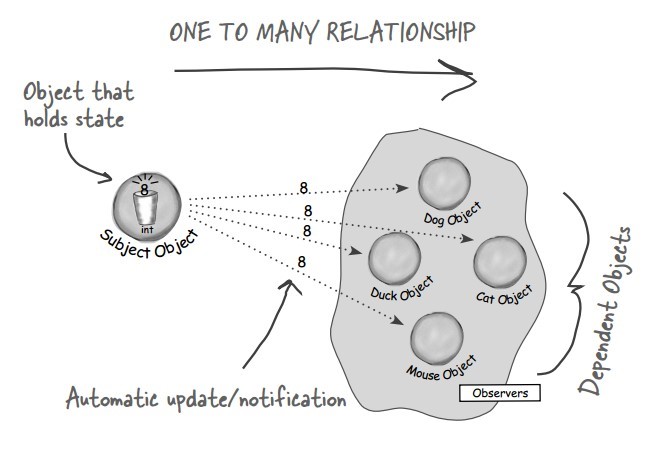
+
+### Class Diagram
+
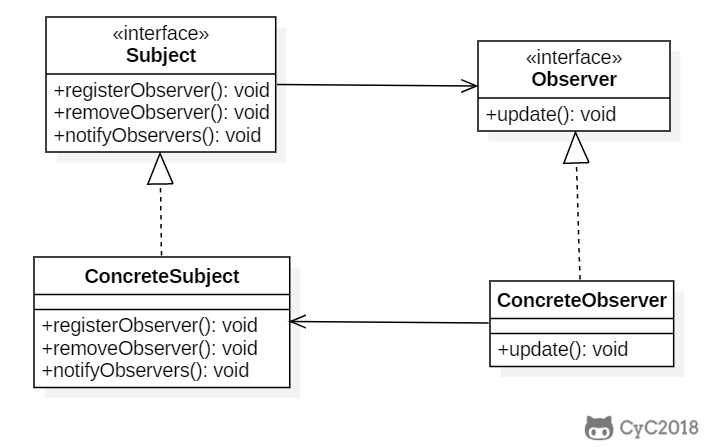
+主题(Subject)具有注册和移除观察者、并通知所有观察者的功能,主题是通过维护一张观察者列表来实现这些操作的。
+
+观察者(Observer)的注册功能需要调用主题的 registerObserver() 方法。
+
+ 
+
+### Implementation
+
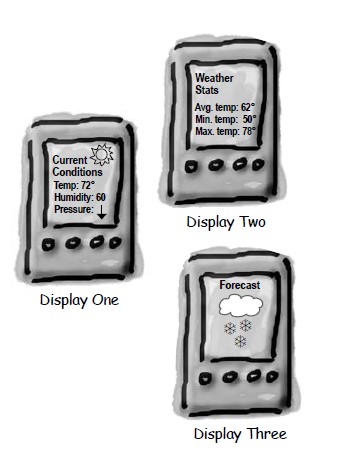
+天气数据布告板会在天气信息发生改变时更新其内容,布告板有多个,并且在将来会继续增加。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface Subject {
+ void registerObserver(Observer o);
+
+ void removeObserver(Observer o);
+
+ void notifyObserver();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class WeatherData implements Subject {
+ private List observers;
+ private float temperature;
+ private float humidity;
+ private float pressure;
+
+ public WeatherData() {
+ observers = new ArrayList<>();
+ }
+
+ public void setMeasurements(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
+ this.temperature = temperature;
+ this.humidity = humidity;
+ this.pressure = pressure;
+ notifyObserver();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void registerObserver(Observer o) {
+ observers.add(o);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
+ int i = observers.indexOf(o);
+ if (i >= 0) {
+ observers.remove(i);
+ }
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void notifyObserver() {
+ for (Observer o : observers) {
+ o.update(temperature, humidity, pressure);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Observer {
+ void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class StatisticsDisplay implements Observer {
+
+ public StatisticsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
+ weatherData.reisterObserver(this);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
+ System.out.println("StatisticsDisplay.update: " + temp + " " + humidity + " " + pressure);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer {
+
+ public CurrentConditionsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
+ weatherData.registerObserver(this);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
+ System.out.println("CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: " + temp + " " + humidity + " " + pressure);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class WeatherStation {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
+ CurrentConditionsDisplay currentConditionsDisplay = new CurrentConditionsDisplay(weatherData);
+ StatisticsDisplay statisticsDisplay = new StatisticsDisplay(weatherData);
+
+ weatherData.setMeasurements(0, 0, 0);
+ weatherData.setMeasurements(1, 1, 1);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: 0.0 0.0 0.0
+StatisticsDisplay.update: 0.0 0.0 0.0
+CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: 1.0 1.0 1.0
+StatisticsDisplay.update: 1.0 1.0 1.0
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Observer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Observer.html)
+- [java.util.EventListener](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/EventListener.html)
+- [javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener](http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/servlet/http/HttpSessionBindingListener.html)
+- [RxJava](https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxJava)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
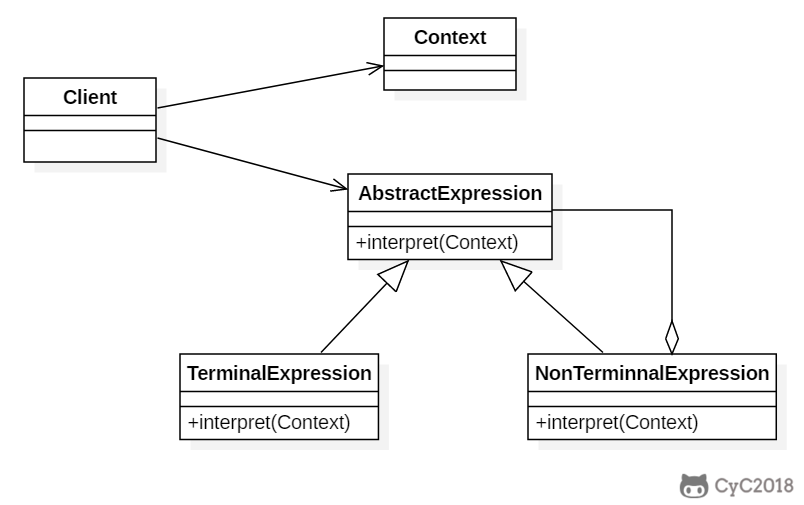
+
+### Implementation
+
+以下是一个规则检验器实现,具有 and 和 or 规则,通过规则可以构建一颗解析树,用来检验一个文本是否满足解析树定义的规则。
+
+例如一颗解析树为 D And (A Or (B C)),文本 "D A" 满足该解析树定义的规则。
+
+这里的 Context 指的是 String。
+
+```java
+public abstract class Expression {
+ public abstract boolean interpret(String str);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class TerminalExpression extends Expression {
+
+ private String literal = null;
+
+ public TerminalExpression(String str) {
+ literal = str;
+ }
+
+ public boolean interpret(String str) {
+ StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(str);
+ while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
+ String test = st.nextToken();
+ if (test.equals(literal)) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class AndExpression extends Expression {
+
+ private Expression expression1 = null;
+ private Expression expression2 = null;
+
+ public AndExpression(Expression expression1, Expression expression2) {
+ this.expression1 = expression1;
+ this.expression2 = expression2;
+ }
+
+ public boolean interpret(String str) {
+ return expression1.interpret(str) && expression2.interpret(str);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class OrExpression extends Expression {
+ private Expression expression1 = null;
+ private Expression expression2 = null;
+
+ public OrExpression(Expression expression1, Expression expression2) {
+ this.expression1 = expression1;
+ this.expression2 = expression2;
+ }
+
+ public boolean interpret(String str) {
+ return expression1.interpret(str) || expression2.interpret(str);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ /**
+ * 构建解析树
+ */
+ public static Expression buildInterpreterTree() {
+ // Literal
+ Expression terminal1 = new TerminalExpression("A");
+ Expression terminal2 = new TerminalExpression("B");
+ Expression terminal3 = new TerminalExpression("C");
+ Expression terminal4 = new TerminalExpression("D");
+ // B C
+ Expression alternation1 = new OrExpression(terminal2, terminal3);
+ // A Or (B C)
+ Expression alternation2 = new OrExpression(terminal1, alternation1);
+ // D And (A Or (B C))
+ return new AndExpression(terminal4, alternation2);
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Expression define = buildInterpreterTree();
+ String context1 = "D A";
+ String context2 = "A B";
+ System.out.println(define.interpret(context1));
+ System.out.println(define.interpret(context2));
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+true
+false
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Pattern](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/regex/Pattern.html)
+- [java.text.Normalizer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/text/Normalizer.html)
+- All subclasses of [java.text.Format](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/text/Format.html)
+- [javax.el.ELResolver](http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/el/ELResolver.html)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
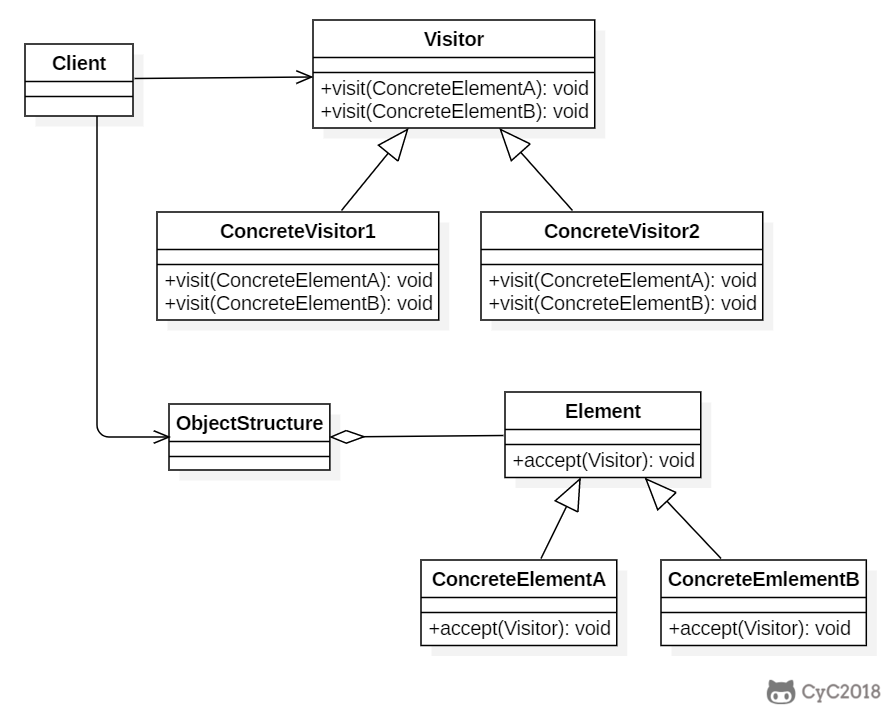
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Element {
+ void accept(Visitor visitor);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+class CustomerGroup {
+
+ private List customers = new ArrayList<>();
+
+ void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ for (Customer customer : customers) {
+ customer.accept(visitor);
+ }
+ }
+
+ void addCustomer(Customer customer) {
+ customers.add(customer);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Customer implements Element {
+
+ private String name;
+ private List orders = new ArrayList<>();
+
+ Customer(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ void addOrder(Order order) {
+ orders.add(order);
+ }
+
+ public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ visitor.visit(this);
+ for (Order order : orders) {
+ order.accept(visitor);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Order implements Element {
+
+ private String name;
+ private List- items = new ArrayList();
+
+ Order(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ Order(String name, String itemName) {
+ this.name = name;
+ this.addItem(new Item(itemName));
+ }
+
+ String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ void addItem(Item item) {
+ items.add(item);
+ }
+
+ public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ visitor.visit(this);
+
+ for (Item item : items) {
+ item.accept(visitor);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Item implements Element {
+
+ private String name;
+
+ Item(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ visitor.visit(this);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Visitor {
+ void visit(Customer customer);
+
+ void visit(Order order);
+
+ void visit(Item item);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class GeneralReport implements Visitor {
+
+ private int customersNo;
+ private int ordersNo;
+ private int itemsNo;
+
+ public void visit(Customer customer) {
+ System.out.println(customer.getName());
+ customersNo++;
+ }
+
+ public void visit(Order order) {
+ System.out.println(order.getName());
+ ordersNo++;
+ }
+
+ public void visit(Item item) {
+ System.out.println(item.getName());
+ itemsNo++;
+ }
+
+ public void displayResults() {
+ System.out.println("Number of customers: " + customersNo);
+ System.out.println("Number of orders: " + ordersNo);
+ System.out.println("Number of items: " + itemsNo);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Customer customer1 = new Customer("customer1");
+ customer1.addOrder(new Order("order1", "item1"));
+ customer1.addOrder(new Order("order2", "item1"));
+ customer1.addOrder(new Order("order3", "item1"));
+
+ Order order = new Order("order_a");
+ order.addItem(new Item("item_a1"));
+ order.addItem(new Item("item_a2"));
+ order.addItem(new Item("item_a3"));
+ Customer customer2 = new Customer("customer2");
+ customer2.addOrder(order);
+
+ CustomerGroup customers = new CustomerGroup();
+ customers.addCustomer(customer1);
+ customers.addCustomer(customer2);
+
+ GeneralReport visitor = new GeneralReport();
+ customers.accept(visitor);
+ visitor.displayResults();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+customer1
+order1
+item1
+order2
+item1
+order3
+item1
+customer2
+order_a
+item_a1
+item_a2
+item_a3
+Number of customers: 2
+Number of orders: 4
+Number of items: 6
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- javax.lang.model.element.Element and javax.lang.model.element.ElementVisitor
+- javax.lang.model.type.TypeMirror and javax.lang.model.type.TypeVisitor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

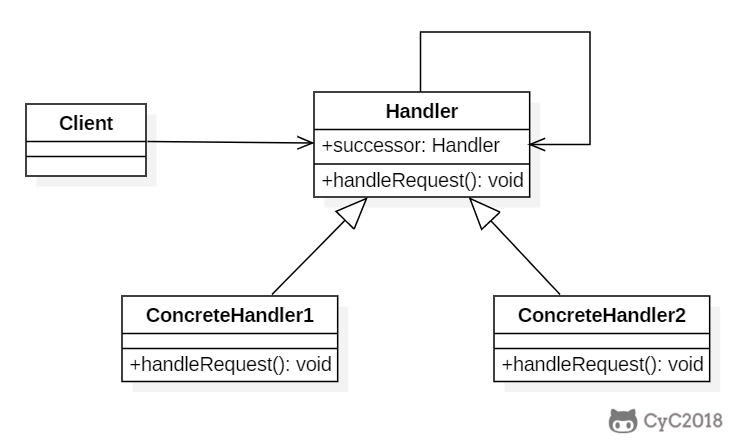
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class Handler {
+
+ protected Handler successor;
+
+
+ public Handler(Handler successor) {
+ this.successor = successor;
+ }
+
+
+ protected abstract void handleRequest(Request request);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteHandler1 extends Handler {
+
+ public ConcreteHandler1(Handler successor) {
+ super(successor);
+ }
+
+
+ @Override
+ protected void handleRequest(Request request) {
+ if (request.getType() == RequestType.TYPE1) {
+ System.out.println(request.getName() + " is handle by ConcreteHandler1");
+ return;
+ }
+ if (successor != null) {
+ successor.handleRequest(request);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteHandler2 extends Handler {
+
+ public ConcreteHandler2(Handler successor) {
+ super(successor);
+ }
+
+
+ @Override
+ protected void handleRequest(Request request) {
+ if (request.getType() == RequestType.TYPE2) {
+ System.out.println(request.getName() + " is handle by ConcreteHandler2");
+ return;
+ }
+ if (successor != null) {
+ successor.handleRequest(request);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Request {
+
+ private RequestType type;
+ private String name;
+
+
+ public Request(RequestType type, String name) {
+ this.type = type;
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+
+ public RequestType getType() {
+ return type;
+ }
+
+
+ public String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+```java
+public enum RequestType {
+ TYPE1, TYPE2
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+
+ Handler handler1 = new ConcreteHandler1(null);
+ Handler handler2 = new ConcreteHandler2(handler1);
+
+ Request request1 = new Request(RequestType.TYPE1, "request1");
+ handler2.handleRequest(request1);
+
+ Request request2 = new Request(RequestType.TYPE2, "request2");
+ handler2.handleRequest(request2);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+request1 is handle by ConcreteHandler1
+request2 is handle by ConcreteHandler2
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.logging.Logger#log()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/logging/Logger.html#log%28java.util.logging.Level,%20java.lang.String%29)
+- [Apache Commons Chain](https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-chain/index.html)
+- [javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter()](http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/servlet/Filter.html#doFilter-javax.servlet.ServletRequest-javax.servlet.ServletResponse-javax.servlet.FilterChain-)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
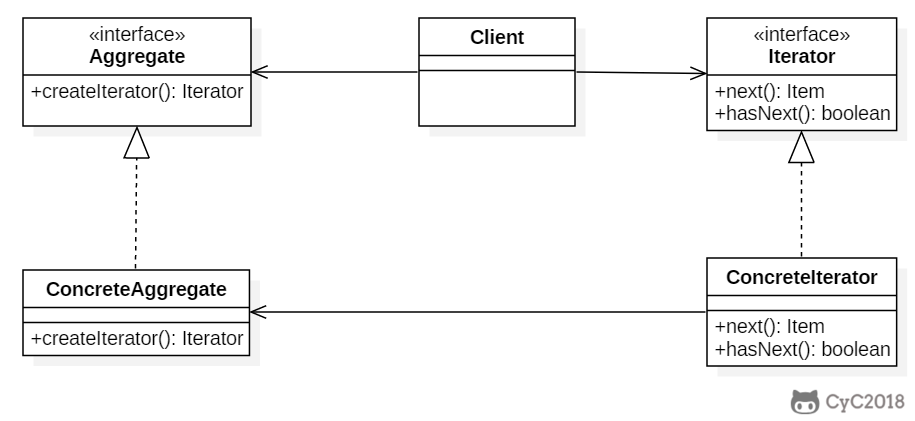
+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Aggregate {
+ Iterator createIterator();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteAggregate implements Aggregate {
+
+ private Integer[] items;
+
+ public ConcreteAggregate() {
+ items = new Integer[10];
+ for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
+ items[i] = i;
+ }
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public Iterator createIterator() {
+ return new ConcreteIterator(items);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Iterator- {
+
+ Item next();
+
+ boolean hasNext();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteIterator
- implements Iterator {
+
+ private Item[] items;
+ private int position = 0;
+
+ public ConcreteIterator(Item[] items) {
+ this.items = items;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public Object next() {
+ return items[position++];
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public boolean hasNext() {
+ return position < items.length;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Aggregate aggregate = new ConcreteAggregate();
+ Iterator iterator = aggregate.createIterator();
+ while (iterator.hasNext()) {
+ System.out.println(iterator.next());
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Iterator](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html)
+- [java.util.Enumeration](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Enumeration.html)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs/notes/设计模式 - 适配器.md b/docs/notes/设计模式 - 适配器.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..102ff5f0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/notes/设计模式 - 适配器.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+## 1. 适配器(Adapter)
+
+### Intent
+
+把一个类接口转换成另一个用户需要的接口。
+
+
+
+### Class Diagram
+
+
+
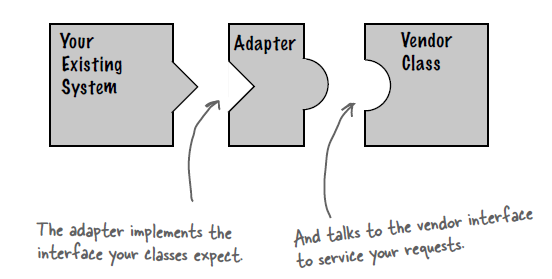
+### Implementation
+
+鸭子(Duck)和火鸡(Turkey)拥有不同的叫声,Duck 的叫声调用 quack() 方法,而 Turkey 调用 gobble() 方法。
+
+要求将 Turkey 的 gobble() 方法适配成 Duck 的 quack() 方法,从而让火鸡冒充鸭子!
+
+```java
+public interface Duck {
+ void quack();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Turkey {
+ void gobble();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class WildTurkey implements Turkey {
+ @Override
+ public void gobble() {
+ System.out.println("gobble!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class TurkeyAdapter implements Duck {
+ Turkey turkey;
+
+ public TurkeyAdapter(Turkey turkey) {
+ this.turkey = turkey;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void quack() {
+ turkey.gobble();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Turkey turkey = new WildTurkey();
+ Duck duck = new TurkeyAdapter(turkey);
+ duck.quack();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Arrays#asList()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Arrays.html#asList%28T...%29)
+- [java.util.Collections#list()](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Collections.html#list-java.util.Enumeration-)
+- [java.util.Collections#enumeration()](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Collections.html#enumeration-java.util.Collection-)
+- [javax.xml.bind.annotation.adapters.XMLAdapter](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/bind/annotation/adapters/XmlAdapter.html#marshal-BoundType-)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/notes/设计模式 - 单例.md b/notes/设计模式 - 单例.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..136b0f0e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/notes/设计模式 - 单例.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+## 单例(Singleton)
+
+### Intent
+
+确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供该实例的全局访问点。
+
+### Class Diagram
+
+使用一个私有构造函数、一个私有静态变量以及一个公有静态函数来实现。
+
+私有构造函数保证了不能通过构造函数来创建对象实例,只能通过公有静态函数返回唯一的私有静态变量。
+
+
+
+### Implementation
+
+#### Ⅰ 懒汉式-线程不安全
+
+以下实现中,私有静态变量 uniqueInstance 被延迟实例化,这样做的好处是,如果没有用到该类,那么就不会实例化 uniqueInstance,从而节约资源。
+
+这个实现在多线程环境下是不安全的,如果多个线程能够同时进入 `if (uniqueInstance == null)` ,并且此时 uniqueInstance 为 null,那么会有多个线程执行 `uniqueInstance = new Singleton();` 语句,这将导致实例化多次 uniqueInstance。
+
+```java
+public class Singleton {
+
+ private static Singleton uniqueInstance;
+
+ private Singleton() {
+ }
+
+ public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+ return uniqueInstance;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### Ⅱ 饿汉式-线程安全
+
+线程不安全问题主要是由于 uniqueInstance 被实例化多次,采取直接实例化 uniqueInstance 的方式就不会产生线程不安全问题。
+
+但是直接实例化的方式也丢失了延迟实例化带来的节约资源的好处。
+
+```java
+private static Singleton uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+```
+
+#### Ⅲ 懒汉式-线程安全
+
+只需要对 getUniqueInstance() 方法加锁,那么在一个时间点只能有一个线程能够进入该方法,从而避免了实例化多次 uniqueInstance。
+
+但是当一个线程进入该方法之后,其它试图进入该方法的线程都必须等待,即使 uniqueInstance 已经被实例化了。这会让线程阻塞时间过长,因此该方法有性能问题,不推荐使用。
+
+```java
+public static synchronized Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+ return uniqueInstance;
+}
+```
+
+#### Ⅳ 双重校验锁-线程安全
+
+uniqueInstance 只需要被实例化一次,之后就可以直接使用了。加锁操作只需要对实例化那部分的代码进行,只有当 uniqueInstance 没有被实例化时,才需要进行加锁。
+
+双重校验锁先判断 uniqueInstance 是否已经被实例化,如果没有被实例化,那么才对实例化语句进行加锁。
+
+```java
+public class Singleton {
+
+ private volatile static Singleton uniqueInstance;
+
+ private Singleton() {
+ }
+
+ public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ synchronized (Singleton.class) {
+ if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return uniqueInstance;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+考虑下面的实现,也就是只使用了一个 if 语句。在 uniqueInstance == null 的情况下,如果两个线程都执行了 if 语句,那么两个线程都会进入 if 语句块内。虽然在 if 语句块内有加锁操作,但是两个线程都会执行 `uniqueInstance = new Singleton();` 这条语句,只是先后的问题,那么就会进行两次实例化。因此必须使用双重校验锁,也就是需要使用两个 if 语句:第一个 if 语句用来避免 uniqueInstance 已经被实例化之后的加锁操作,而第二个 if 语句进行了加锁,所以只能有一个线程进入,就不会出现 uniqueInstance == null 时两个线程同时进行实例化操作。
+
+```java
+if (uniqueInstance == null) {
+ synchronized (Singleton.class) {
+ uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+uniqueInstance 采用 volatile 关键字修饰也是很有必要的, `uniqueInstance = new Singleton();` 这段代码其实是分为三步执行:
+
+1. 为 uniqueInstance 分配内存空间
+2. 初始化 uniqueInstance
+3. 将 uniqueInstance 指向分配的内存地址
+
+但是由于 JVM 具有指令重排的特性,执行顺序有可能变成 1>3>2。指令重排在单线程环境下不会出现问题,但是在多线程环境下会导致一个线程获得还没有初始化的实例。例如,线程 T1 执行了 1 和 3,此时 T2 调用 getUniqueInstance() 后发现 uniqueInstance 不为空,因此返回 uniqueInstance,但此时 uniqueInstance 还未被初始化。
+
+使用 volatile 可以禁止 JVM 的指令重排,保证在多线程环境下也能正常运行。
+
+#### Ⅴ 静态内部类实现
+
+当 Singleton 类被加载时,静态内部类 SingletonHolder 没有被加载进内存。只有当调用 `getUniqueInstance()` 方法从而触发 `SingletonHolder.INSTANCE` 时 SingletonHolder 才会被加载,此时初始化 INSTANCE 实例,并且 JVM 能确保 INSTANCE 只被实例化一次。
+
+这种方式不仅具有延迟初始化的好处,而且由 JVM 提供了对线程安全的支持。
+
+```java
+public class Singleton {
+
+ private Singleton() {
+ }
+
+ private static class SingletonHolder {
+ private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
+ }
+
+ public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
+ return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### Ⅵ 枚举实现
+
+```java
+public enum Singleton {
+
+ INSTANCE;
+
+ private String objName;
+
+
+ public String getObjName() {
+ return objName;
+ }
+
+
+ public void setObjName(String objName) {
+ this.objName = objName;
+ }
+
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+
+ // 单例测试
+ Singleton firstSingleton = Singleton.INSTANCE;
+ firstSingleton.setObjName("firstName");
+ System.out.println(firstSingleton.getObjName());
+ Singleton secondSingleton = Singleton.INSTANCE;
+ secondSingleton.setObjName("secondName");
+ System.out.println(firstSingleton.getObjName());
+ System.out.println(secondSingleton.getObjName());
+
+ // 反射获取实例测试
+ try {
+ Singleton[] enumConstants = Singleton.class.getEnumConstants();
+ for (Singleton enumConstant : enumConstants) {
+ System.out.println(enumConstant.getObjName());
+ }
+ } catch (Exception e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+firstName
+secondName
+secondName
+secondName
+```
+
+该实现可以防止反射攻击。在其它实现中,通过 setAccessible() 方法可以将私有构造函数的访问级别设置为 public,然后调用构造函数从而实例化对象,如果要防止这种攻击,需要在构造函数中添加防止多次实例化的代码。该实现是由 JVM 保证只会实例化一次,因此不会出现上述的反射攻击。
+
+该实现在多次序列化和序列化之后,不会得到多个实例。而其它实现需要使用 transient 修饰所有字段,并且实现序列化和反序列化的方法。
+
+### Examples
+
+- Logger Classes
+- Configuration Classes
+- Accesing resources in shared mode
+- Factories implemented as Singletons
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.Runtime#getRuntime()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Runtime.html#getRuntime%28%29)
+- [java.awt.Desktop#getDesktop()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/awt/Desktop.html#getDesktop--)
+- [java.lang.System#getSecurityManager()](
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+Alarm(闹钟)、CoffeePot(咖啡壶)、Calendar(日历)、Sprinkler(喷头)是一组相关的对象,在某个对象的事件产生时需要去操作其它对象,形成了下面这种依赖结构:
+
+ 
+
+使用中介者模式可以将复杂的依赖结构变成星形结构:
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public abstract class Colleague {
+ public abstract void onEvent(Mediator mediator);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Alarm extends Colleague {
+
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("alarm");
+ }
+
+ public void doAlarm() {
+ System.out.println("doAlarm()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class CoffeePot extends Colleague {
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("coffeePot");
+ }
+
+ public void doCoffeePot() {
+ System.out.println("doCoffeePot()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Calender extends Colleague {
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("calender");
+ }
+
+ public void doCalender() {
+ System.out.println("doCalender()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Sprinkler extends Colleague {
+ @Override
+ public void onEvent(Mediator mediator) {
+ mediator.doEvent("sprinkler");
+ }
+
+ public void doSprinkler() {
+ System.out.println("doSprinkler()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class Mediator {
+ public abstract void doEvent(String eventType);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteMediator extends Mediator {
+ private Alarm alarm;
+ private CoffeePot coffeePot;
+ private Calender calender;
+ private Sprinkler sprinkler;
+
+ public ConcreteMediator(Alarm alarm, CoffeePot coffeePot, Calender calender, Sprinkler sprinkler) {
+ this.alarm = alarm;
+ this.coffeePot = coffeePot;
+ this.calender = calender;
+ this.sprinkler = sprinkler;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void doEvent(String eventType) {
+ switch (eventType) {
+ case "alarm":
+ doAlarmEvent();
+ break;
+ case "coffeePot":
+ doCoffeePotEvent();
+ break;
+ case "calender":
+ doCalenderEvent();
+ break;
+ default:
+ doSprinklerEvent();
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void doAlarmEvent() {
+ alarm.doAlarm();
+ coffeePot.doCoffeePot();
+ calender.doCalender();
+ sprinkler.doSprinkler();
+ }
+
+ public void doCoffeePotEvent() {
+ // ...
+ }
+
+ public void doCalenderEvent() {
+ // ...
+ }
+
+ public void doSprinklerEvent() {
+ // ...
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Alarm alarm = new Alarm();
+ CoffeePot coffeePot = new CoffeePot();
+ Calender calender = new Calender();
+ Sprinkler sprinkler = new Sprinkler();
+ Mediator mediator = new ConcreteMediator(alarm, coffeePot, calender, sprinkler);
+ // 闹钟事件到达,调用中介者就可以操作相关对象
+ alarm.onEvent(mediator);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+doAlarm()
+doCoffeePot()
+doCalender()
+doSprinkler()
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- All scheduleXXX() methods of [java.util.Timer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Timer.html)
+- [java.util.concurrent.Executor#execute()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/Executor.html#execute-java.lang.Runnable-)
+- submit() and invokeXXX() methods of [java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/ExecutorService.html)
+- scheduleXXX() methods of [java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/ScheduledExecutorService.html)
+- [java.lang.reflect.Method#invoke()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/reflect/Method.html#invoke-java.lang.Object-java.lang.Object...-)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Flyweight {
+ void doOperation(String extrinsicState);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFlyweight implements Flyweight {
+
+ private String intrinsicState;
+
+ public ConcreteFlyweight(String intrinsicState) {
+ this.intrinsicState = intrinsicState;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void doOperation(String extrinsicState) {
+ System.out.println("Object address: " + System.identityHashCode(this));
+ System.out.println("IntrinsicState: " + intrinsicState);
+ System.out.println("ExtrinsicState: " + extrinsicState);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class FlyweightFactory {
+
+ private HashMap flyweights = new HashMap<>();
+
+ Flyweight getFlyweight(String intrinsicState) {
+ if (!flyweights.containsKey(intrinsicState)) {
+ Flyweight flyweight = new ConcreteFlyweight(intrinsicState);
+ flyweights.put(intrinsicState, flyweight);
+ }
+ return flyweights.get(intrinsicState);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory();
+ Flyweight flyweight1 = factory.getFlyweight("aa");
+ Flyweight flyweight2 = factory.getFlyweight("aa");
+ flyweight1.doOperation("x");
+ flyweight2.doOperation("y");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+Object address: 1163157884
+IntrinsicState: aa
+ExtrinsicState: x
+Object address: 1163157884
+IntrinsicState: aa
+ExtrinsicState: y
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+Java 利用缓存来加速大量小对象的访问时间。
+
+- java.lang.Integer#valueOf(int)
+- java.lang.Boolean#valueOf(boolean)
+- java.lang.Byte#valueOf(byte)
+- java.lang.Character#valueOf(char)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+以下是一个虚拟代理的实现,模拟了图片延迟加载的情况下使用与图片大小相等的临时内容去替换原始图片,直到图片加载完成才将图片显示出来。
+
+```java
+public interface Image {
+ void showImage();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class HighResolutionImage implements Image {
+
+ private URL imageURL;
+ private long startTime;
+ private int height;
+ private int width;
+
+ public int getHeight() {
+ return height;
+ }
+
+ public int getWidth() {
+ return width;
+ }
+
+ public HighResolutionImage(URL imageURL) {
+ this.imageURL = imageURL;
+ this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
+ this.width = 600;
+ this.height = 600;
+ }
+
+ public boolean isLoad() {
+ // 模拟图片加载,延迟 3s 加载完成
+ long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
+ return endTime - startTime > 3000;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void showImage() {
+ System.out.println("Real Image: " + imageURL);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ImageProxy implements Image {
+
+ private HighResolutionImage highResolutionImage;
+
+ public ImageProxy(HighResolutionImage highResolutionImage) {
+ this.highResolutionImage = highResolutionImage;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void showImage() {
+ while (!highResolutionImage.isLoad()) {
+ try {
+ System.out.println("Temp Image: " + highResolutionImage.getWidth() + " " + highResolutionImage.getHeight());
+ Thread.sleep(100);
+ } catch (InterruptedException e) {
+ e.printStackTrace();
+ }
+ }
+ highResolutionImage.showImage();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ImageViewer {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
+ String image = "http://image.jpg";
+ URL url = new URL(image);
+ HighResolutionImage highResolutionImage = new HighResolutionImage(url);
+ ImageProxy imageProxy = new ImageProxy(highResolutionImage);
+ imageProxy.showImage();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.lang.reflect.Proxy
+- RMI
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class Prototype {
+ abstract Prototype myClone();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcretePrototype extends Prototype {
+
+ private String filed;
+
+ public ConcretePrototype(String filed) {
+ this.filed = filed;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ Prototype myClone() {
+ return new ConcretePrototype(filed);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public String toString() {
+ return filed;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Prototype prototype = new ConcretePrototype("abc");
+ Prototype clone = prototype.myClone();
+ System.out.println(clone.toString());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+abc
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.Object#clone()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Object.html#clone%28%29)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+设计一个遥控器,可以控制电灯开关。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface Command {
+ void execute();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class LightOnCommand implements Command {
+ Light light;
+
+ public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
+ this.light = light;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void execute() {
+ light.on();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class LightOffCommand implements Command {
+ Light light;
+
+ public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
+ this.light = light;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void execute() {
+ light.off();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Light {
+
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("Light is on!");
+ }
+
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("Light is off!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * 遥控器
+ */
+public class Invoker {
+ private Command[] onCommands;
+ private Command[] offCommands;
+ private final int slotNum = 7;
+
+ public Invoker() {
+ this.onCommands = new Command[slotNum];
+ this.offCommands = new Command[slotNum];
+ }
+
+ public void setOnCommand(Command command, int slot) {
+ onCommands[slot] = command;
+ }
+
+ public void setOffCommand(Command command, int slot) {
+ offCommands[slot] = command;
+ }
+
+ public void onButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
+ onCommands[slot].execute();
+ }
+
+ public void offButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
+ offCommands[slot].execute();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Invoker invoker = new Invoker();
+ Light light = new Light();
+ Command lightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(light);
+ Command lightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(light);
+ invoker.setOnCommand(lightOnCommand, 0);
+ invoker.setOffCommand(lightOffCommand, 0);
+ invoker.onButtonWasPushed(0);
+ invoker.offButtonWasPushed(0);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.Runnable](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Runnable.html)
+- [Netflix Hystrix](https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki)
+- [javax.swing.Action](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/swing/Action.html)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+以下实现了一个简单计算器程序,可以输入两个值,然后计算这两个值的和。备忘录模式允许将这两个值存储起来,然后在某个时刻用存储的状态进行恢复。
+
+实现参考:[Memento Pattern - Calculator Example - Java Sourcecode](https://www.oodesign.com/memento-pattern-calculator-example-java-sourcecode.html)
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Originator Interface
+ */
+public interface Calculator {
+
+ // Create Memento
+ PreviousCalculationToCareTaker backupLastCalculation();
+
+ // setMemento
+ void restorePreviousCalculation(PreviousCalculationToCareTaker memento);
+
+ int getCalculationResult();
+
+ void setFirstNumber(int firstNumber);
+
+ void setSecondNumber(int secondNumber);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Originator Implementation
+ */
+public class CalculatorImp implements Calculator {
+
+ private int firstNumber;
+ private int secondNumber;
+
+ @Override
+ public PreviousCalculationToCareTaker backupLastCalculation() {
+ // create a memento object used for restoring two numbers
+ return new PreviousCalculationImp(firstNumber, secondNumber);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void restorePreviousCalculation(PreviousCalculationToCareTaker memento) {
+ this.firstNumber = ((PreviousCalculationToOriginator) memento).getFirstNumber();
+ this.secondNumber = ((PreviousCalculationToOriginator) memento).getSecondNumber();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int getCalculationResult() {
+ // result is adding two numbers
+ return firstNumber + secondNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void setFirstNumber(int firstNumber) {
+ this.firstNumber = firstNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void setSecondNumber(int secondNumber) {
+ this.secondNumber = secondNumber;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Memento Interface to Originator
+ *
+ * This interface allows the originator to restore its state
+ */
+public interface PreviousCalculationToOriginator {
+ int getFirstNumber();
+ int getSecondNumber();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Memento interface to CalculatorOperator (Caretaker)
+ */
+public interface PreviousCalculationToCareTaker {
+ // no operations permitted for the caretaker
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * Memento Object Implementation
+ *
+ * Note that this object implements both interfaces to Originator and CareTaker
+ */
+public class PreviousCalculationImp implements PreviousCalculationToCareTaker,
+ PreviousCalculationToOriginator {
+
+ private int firstNumber;
+ private int secondNumber;
+
+ public PreviousCalculationImp(int firstNumber, int secondNumber) {
+ this.firstNumber = firstNumber;
+ this.secondNumber = secondNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int getFirstNumber() {
+ return firstNumber;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int getSecondNumber() {
+ return secondNumber;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+/**
+ * CareTaker object
+ */
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ // program starts
+ Calculator calculator = new CalculatorImp();
+
+ // assume user enters two numbers
+ calculator.setFirstNumber(10);
+ calculator.setSecondNumber(100);
+
+ // find result
+ System.out.println(calculator.getCalculationResult());
+
+ // Store result of this calculation in case of error
+ PreviousCalculationToCareTaker memento = calculator.backupLastCalculation();
+
+ // user enters a number
+ calculator.setFirstNumber(17);
+
+ // user enters a wrong second number and calculates result
+ calculator.setSecondNumber(-290);
+
+ // calculate result
+ System.out.println(calculator.getCalculationResult());
+
+ // user hits CTRL + Z to undo last operation and see last result
+ calculator.restorePreviousCalculation(memento);
+
+ // result restored
+ System.out.println(calculator.getCalculationResult());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+110
+-273
+110
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.io.Serializable
+
+
+
+
+
+
+


+
+### Implementation
+
+观看电影需要操作很多电器,使用外观模式实现一键看电影功能。
+
+```java
+public class SubSystem {
+ public void turnOnTV() {
+ System.out.println("turnOnTV()");
+ }
+
+ public void setCD(String cd) {
+ System.out.println("setCD( " + cd + " )");
+ }
+
+ public void startWatching(){
+ System.out.println("startWatching()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Facade {
+ private SubSystem subSystem = new SubSystem();
+
+ public void watchMovie() {
+ subSystem.turnOnTV();
+ subSystem.setCD("a movie");
+ subSystem.startWatching();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Facade facade = new Facade();
+ facade.watchMovie();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### 设计原则
+
+最少知识原则:只和你的密友谈话。也就是说客户对象所需要交互的对象应当尽可能少。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class Factory {
+ abstract public Product factoryMethod();
+ public void doSomething() {
+ Product product = factoryMethod();
+ // do something with the product
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory extends Factory {
+ public Product factoryMethod() {
+ return new ConcreteProduct();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory1 extends Factory {
+ public Product factoryMethod() {
+ return new ConcreteProduct1();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory2 extends Factory {
+ public Product factoryMethod() {
+ return new ConcreteProduct2();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Calendar](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Calendar.html#getInstance--)
+- [java.util.ResourceBundle](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/ResourceBundle.html#getBundle-java.lang.String-)
+- [java.text.NumberFormat](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/text/NumberFormat.html#getInstance--)
+- [java.nio.charset.Charset](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/charset/Charset.html#forName-java.lang.String-)
+- [java.net.URLStreamHandlerFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/net/URLStreamHandlerFactory.html#createURLStreamHandler-java.lang.String-)
+- [java.util.EnumSet](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/EnumSet.html#of-E-)
+- [javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/bind/JAXBContext.html#createMarshaller--)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public class AbstractProductA {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class AbstractProductB {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductA1 extends AbstractProductA {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductA2 extends AbstractProductA {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductB1 extends AbstractProductB {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ProductB2 extends AbstractProductB {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class AbstractFactory {
+ abstract AbstractProductA createProductA();
+ abstract AbstractProductB createProductB();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory1 extends AbstractFactory {
+ AbstractProductA createProductA() {
+ return new ProductA1();
+ }
+
+ AbstractProductB createProductB() {
+ return new ProductB1();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteFactory2 extends AbstractFactory {
+ AbstractProductA createProductA() {
+ return new ProductA2();
+ }
+
+ AbstractProductB createProductB() {
+ return new ProductB2();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ AbstractFactory abstractFactory = new ConcreteFactory1();
+ AbstractProductA productA = abstractFactory.createProductA();
+ AbstractProductB productB = abstractFactory.createProductB();
+ // do something with productA and productB
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/parsers/DocumentBuilderFactory.html)
+- [javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/transform/TransformerFactory.html#newInstance--)
+- [javax.xml.xpath.XPathFactory](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/xpath/XPathFactory.html#newInstance--)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+RemoteControl 表示遥控器,指代 Abstraction。
+
+TV 表示电视,指代 Implementor。
+
+桥接模式将遥控器和电视分离开来,从而可以独立改变遥控器或者电视的实现。
+
+```java
+public abstract class TV {
+ public abstract void on();
+
+ public abstract void off();
+
+ public abstract void tuneChannel();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Sony extends TV {
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("Sony.on()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("Sony.off()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("Sony.tuneChannel()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class RCA extends TV {
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("RCA.on()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("RCA.off()");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("RCA.tuneChannel()");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class RemoteControl {
+ protected TV tv;
+
+ public RemoteControl(TV tv) {
+ this.tv = tv;
+ }
+
+ public abstract void on();
+
+ public abstract void off();
+
+ public abstract void tuneChannel();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteRemoteControl1 extends RemoteControl {
+ public ConcreteRemoteControl1(TV tv) {
+ super(tv);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl1.on()");
+ tv.on();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl1.off()");
+ tv.off();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl1.tuneChannel()");
+ tv.tuneChannel();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteRemoteControl2 extends RemoteControl {
+ public ConcreteRemoteControl2(TV tv) {
+ super(tv);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void on() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl2.on()");
+ tv.on();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void off() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl2.off()");
+ tv.off();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void tuneChannel() {
+ System.out.println("ConcreteRemoteControl2.tuneChannel()");
+ tv.tuneChannel();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ RemoteControl remoteControl1 = new ConcreteRemoteControl1(new RCA());
+ remoteControl1.on();
+ remoteControl1.off();
+ remoteControl1.tuneChannel();
+ RemoteControl remoteControl2 = new ConcreteRemoteControl2(new Sony());
+ remoteControl2.on();
+ remoteControl2.off();
+ remoteControl2.tuneChannel();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- AWT (It provides an abstraction layer which maps onto the native OS the windowing support.)
+- JDBC
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+冲咖啡和冲茶都有类似的流程,但是某些步骤会有点不一样,要求复用那些相同步骤的代码。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public abstract class CaffeineBeverage {
+
+ final void prepareRecipe() {
+ boilWater();
+ brew();
+ pourInCup();
+ addCondiments();
+ }
+
+ abstract void brew();
+
+ abstract void addCondiments();
+
+ void boilWater() {
+ System.out.println("boilWater");
+ }
+
+ void pourInCup() {
+ System.out.println("pourInCup");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Coffee extends CaffeineBeverage {
+ @Override
+ void brew() {
+ System.out.println("Coffee.brew");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void addCondiments() {
+ System.out.println("Coffee.addCondiments");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Tea extends CaffeineBeverage {
+ @Override
+ void brew() {
+ System.out.println("Tea.brew");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void addCondiments() {
+ System.out.println("Tea.addCondiments");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ CaffeineBeverage caffeineBeverage = new Coffee();
+ caffeineBeverage.prepareRecipe();
+ System.out.println("-----------");
+ caffeineBeverage = new Tea();
+ caffeineBeverage.prepareRecipe();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+boilWater
+Coffee.brew
+pourInCup
+Coffee.addCondiments
+-----------
+boilWater
+Tea.brew
+pourInCup
+Tea.addCondiments
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.util.Collections#sort()
+- java.io.InputStream#skip()
+- java.io.InputStream#read()
+- java.util.AbstractList#indexOf()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+糖果销售机有多种状态,每种状态下销售机有不同的行为,状态可以发生转移,使得销售机的行为也发生改变。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface State {
+ /**
+ * 投入 25 分钱
+ */
+ void insertQuarter();
+
+ /**
+ * 退回 25 分钱
+ */
+ void ejectQuarter();
+
+ /**
+ * 转动曲柄
+ */
+ void turnCrank();
+
+ /**
+ * 发放糖果
+ */
+ void dispense();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class HasQuarterState implements State {
+
+ private GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You can't insert another quarter");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("Quarter returned");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("You turned...");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldState());
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class NoQuarterState implements State {
+
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You insert a quarter");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getHasQuarterState());
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You haven't insert a quarter");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("You turned, but there's no quarter");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ System.out.println("You need to pay first");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class SoldOutState implements State {
+
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public SoldOutState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("You can't eject, you haven't inserted a quarter yet");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("You turned, but there are no gumballs");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class SoldState implements State {
+
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine;
+
+ public SoldState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
+ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a gumball");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ System.out.println("Sorry, you already turned the crank");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ System.out.println("Turning twice doesn't get you another gumball!");
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void dispense() {
+ gumballMachine.releaseBall();
+ if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
+ } else {
+ System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs");
+ gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class GumballMachine {
+
+ private State soldOutState;
+ private State noQuarterState;
+ private State hasQuarterState;
+ private State soldState;
+
+ private State state;
+ private int count = 0;
+
+ public GumballMachine(int numberGumballs) {
+ count = numberGumballs;
+ soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
+ noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
+ hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
+ soldState = new SoldState(this);
+
+ if (numberGumballs > 0) {
+ state = noQuarterState;
+ } else {
+ state = soldOutState;
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void insertQuarter() {
+ state.insertQuarter();
+ }
+
+ public void ejectQuarter() {
+ state.ejectQuarter();
+ }
+
+ public void turnCrank() {
+ state.turnCrank();
+ state.dispense();
+ }
+
+ public void setState(State state) {
+ this.state = state;
+ }
+
+ public void releaseBall() {
+ System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot...");
+ if (count != 0) {
+ count -= 1;
+ }
+ }
+
+ public State getSoldOutState() {
+ return soldOutState;
+ }
+
+ public State getNoQuarterState() {
+ return noQuarterState;
+ }
+
+ public State getHasQuarterState() {
+ return hasQuarterState;
+ }
+
+ public State getSoldState() {
+ return soldState;
+ }
+
+ public int getCount() {
+ return count;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ GumballMachine gumballMachine = new GumballMachine(5);
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.ejectQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.ejectQuarter();
+
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
+ gumballMachine.turnCrank();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You insert a quarter
+Quarter returned
+You turned, but there's no quarter
+You need to pay first
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You haven't insert a quarter
+You insert a quarter
+You can't insert another quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+You insert a quarter
+You turned...
+A gumball comes rolling out the slot...
+Oops, out of gumballs
+You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out
+You turned, but there are no gumballs
+No gumball dispensed
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+以下是一个简易的 StringBuilder 实现,参考了 JDK 1.8 源码。
+
+```java
+public class AbstractStringBuilder {
+ protected char[] value;
+
+ protected int count;
+
+ public AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
+ count = 0;
+ value = new char[capacity];
+ }
+
+ public AbstractStringBuilder append(char c) {
+ ensureCapacityInternal(count + 1);
+ value[count++] = c;
+ return this;
+ }
+
+ private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
+ // overflow-conscious code
+ if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0)
+ expandCapacity(minimumCapacity);
+ }
+
+ void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
+ int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
+ if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
+ newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
+ if (newCapacity < 0) {
+ if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow
+ throw new OutOfMemoryError();
+ newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ }
+ value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class StringBuilder extends AbstractStringBuilder {
+ public StringBuilder() {
+ super(16);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public String toString() {
+ // Create a copy, don't share the array
+ return new String(value, 0, count);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
+ final int count = 26;
+ for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
+ sb.append((char) ('a' + i));
+ }
+ System.out.println(sb.toString());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.lang.StringBuilder](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/StringBuilder.html)
+- [java.nio.ByteBuffer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/ByteBuffer.html#put-byte-)
+- [java.lang.StringBuffer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/StringBuffer.html#append-boolean-)
+- [java.lang.Appendable](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Appendable.html)
+- [Apache Camel builders](https://github.com/apache/camel/tree/0e195428ee04531be27a0b659005e3aa8d159d23/camel-core/src/main/java/org/apache/camel/builder)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+



+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class AbstractOperation {
+ abstract void request();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class RealOperation extends AbstractOperation {
+ @Override
+ void request() {
+ System.out.println("do something");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class NullOperation extends AbstractOperation{
+ @Override
+ void request() {
+ // do nothing
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ AbstractOperation abstractOperation = func(-1);
+ abstractOperation.request();
+ }
+
+ public static AbstractOperation func(int para) {
+ if (para < 0) {
+ return new NullOperation();
+ }
+ return new RealOperation();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### 与状态模式的比较
+
+状态模式的类图和策略模式类似,并且都是能够动态改变对象的行为。但是状态模式是通过状态转移来改变 Context 所组合的 State 对象,而策略模式是通过 Context 本身的决策来改变组合的 Strategy 对象。所谓的状态转移,是指 Context 在运行过程中由于一些条件发生改变而使得 State 对象发生改变,注意必须要是在运行过程中。
+
+状态模式主要是用来解决状态转移的问题,当状态发生转移了,那么 Context 对象就会改变它的行为;而策略模式主要是用来封装一组可以互相替代的算法族,并且可以根据需要动态地去替换 Context 使用的算法。
+
+### Implementation
+
+设计一个鸭子,它可以动态地改变叫声。这里的算法族是鸭子的叫声行为。
+
+```java
+public interface QuackBehavior {
+ void quack();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Quack implements QuackBehavior {
+ @Override
+ public void quack() {
+ System.out.println("quack!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Squeak implements QuackBehavior{
+ @Override
+ public void quack() {
+ System.out.println("squeak!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Duck {
+
+ private QuackBehavior quackBehavior;
+
+ public void performQuack() {
+ if (quackBehavior != null) {
+ quackBehavior.quack();
+ }
+ }
+
+ public void setQuackBehavior(QuackBehavior quackBehavior) {
+ this.quackBehavior = quackBehavior;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Duck duck = new Duck();
+ duck.setQuackBehavior(new Squeak());
+ duck.performQuack();
+ duck.setQuackBehavior(new Quack());
+ duck.performQuack();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+squeak!
+quack!
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.util.Comparator#compare()
+- javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet
+- javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Product {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteProduct implements Product {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
+}
+```
+
+以下的 Client 类包含了实例化的代码,这是一种错误的实现。如果在客户类中存在这种实例化代码,就需要考虑将代码放到简单工厂中。
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ int type = 1;
+ Product product;
+ if (type == 1) {
+ product = new ConcreteProduct1();
+ } else if (type == 2) {
+ product = new ConcreteProduct2();
+ } else {
+ product = new ConcreteProduct();
+ }
+ // do something with the product
+ }
+}
+```
+
+以下的 SimpleFactory 是简单工厂实现,它被所有需要进行实例化的客户类调用。
+
+```java
+public class SimpleFactory {
+
+ public Product createProduct(int type) {
+ if (type == 1) {
+ return new ConcreteProduct1();
+ } else if (type == 2) {
+ return new ConcreteProduct2();
+ }
+ return new ConcreteProduct();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ SimpleFactory simpleFactory = new SimpleFactory();
+ Product product = simpleFactory.createProduct(1);
+ // do something with the product
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class Component {
+ protected String name;
+
+ public Component(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ public void print() {
+ print(0);
+ }
+
+ abstract void print(int level);
+
+ abstract public void add(Component component);
+
+ abstract public void remove(Component component);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Composite extends Component {
+
+ private List child;
+
+ public Composite(String name) {
+ super(name);
+ child = new ArrayList<>();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void print(int level) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
+ System.out.print("--");
+ }
+ System.out.println("Composite:" + name);
+ for (Component component : child) {
+ component.print(level + 1);
+ }
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void add(Component component) {
+ child.add(component);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void remove(Component component) {
+ child.remove(component);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Leaf extends Component {
+ public Leaf(String name) {
+ super(name);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ void print(int level) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
+ System.out.print("--");
+ }
+ System.out.println("left:" + name);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void add(Component component) {
+ throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); // 牺牲透明性换取单一职责原则,这样就不用考虑是叶子节点还是组合节点
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void remove(Component component) {
+ throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Composite root = new Composite("root");
+ Component node1 = new Leaf("1");
+ Component node2 = new Composite("2");
+ Component node3 = new Leaf("3");
+ root.add(node1);
+ root.add(node2);
+ root.add(node3);
+ Component node21 = new Leaf("21");
+ Component node22 = new Composite("22");
+ node2.add(node21);
+ node2.add(node22);
+ Component node221 = new Leaf("221");
+ node22.add(node221);
+ root.print();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+Composite:root
+--left:1
+--Composite:2
+----left:21
+----Composite:22
+------left:221
+--left:3
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- javax.swing.JComponent#add(Component)
+- java.awt.Container#add(Component)
+- java.util.Map#putAll(Map)
+- java.util.List#addAll(Collection)
+- java.util.Set#addAll(Collection)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+设计不同种类的饮料,饮料可以添加配料,比如可以添加牛奶,并且支持动态添加新配料。每增加一种配料,该饮料的价格就会增加,要求计算一种饮料的价格。
+
+下图表示在 DarkRoast 饮料上新增新添加 Mocha 配料,之后又添加了 Whip 配料。DarkRoast 被 Mocha 包裹,Mocha 又被 Whip 包裹。它们都继承自相同父类,都有 cost() 方法,外层类的 cost() 方法调用了内层类的 cost() 方法。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface Beverage {
+ double cost();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class DarkRoast implements Beverage {
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class HouseBlend implements Beverage {
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public abstract class CondimentDecorator implements Beverage {
+ protected Beverage beverage;
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
+
+ public Milk(Beverage beverage) {
+ this.beverage = beverage;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1 + beverage.cost();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Mocha extends CondimentDecorator {
+
+ public Mocha(Beverage beverage) {
+ this.beverage = beverage;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public double cost() {
+ return 1 + beverage.cost();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Beverage beverage = new HouseBlend();
+ beverage = new Mocha(beverage);
+ beverage = new Milk(beverage);
+ System.out.println(beverage.cost());
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+3.0
+```
+
+### 设计原则
+
+类应该对扩展开放,对修改关闭:也就是添加新功能时不需要修改代码。饮料可以动态添加新的配料,而不需要去修改饮料的代码。
+
+不可能把所有的类设计成都满足这一原则,应当把该原则应用于最有可能发生改变的地方。
+
+### JDK
+
+- java.io.BufferedInputStream(InputStream)
+- java.io.DataInputStream(InputStream)
+- java.io.BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream)
+- java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream(OutputStream)
+- java.util.Collections#checked[List|Map|Set|SortedSet|SortedMap]()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Class Diagram
+
+主题(Subject)具有注册和移除观察者、并通知所有观察者的功能,主题是通过维护一张观察者列表来实现这些操作的。
+
+观察者(Observer)的注册功能需要调用主题的 registerObserver() 方法。
+
+ 
+
+### Implementation
+
+天气数据布告板会在天气信息发生改变时更新其内容,布告板有多个,并且在将来会继续增加。
+
+ 
+
+```java
+public interface Subject {
+ void registerObserver(Observer o);
+
+ void removeObserver(Observer o);
+
+ void notifyObserver();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class WeatherData implements Subject {
+ private List observers;
+ private float temperature;
+ private float humidity;
+ private float pressure;
+
+ public WeatherData() {
+ observers = new ArrayList<>();
+ }
+
+ public void setMeasurements(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
+ this.temperature = temperature;
+ this.humidity = humidity;
+ this.pressure = pressure;
+ notifyObserver();
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void registerObserver(Observer o) {
+ observers.add(o);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
+ int i = observers.indexOf(o);
+ if (i >= 0) {
+ observers.remove(i);
+ }
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void notifyObserver() {
+ for (Observer o : observers) {
+ o.update(temperature, humidity, pressure);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Observer {
+ void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class StatisticsDisplay implements Observer {
+
+ public StatisticsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
+ weatherData.reisterObserver(this);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
+ System.out.println("StatisticsDisplay.update: " + temp + " " + humidity + " " + pressure);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer {
+
+ public CurrentConditionsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
+ weatherData.registerObserver(this);
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
+ System.out.println("CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: " + temp + " " + humidity + " " + pressure);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class WeatherStation {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
+ CurrentConditionsDisplay currentConditionsDisplay = new CurrentConditionsDisplay(weatherData);
+ StatisticsDisplay statisticsDisplay = new StatisticsDisplay(weatherData);
+
+ weatherData.setMeasurements(0, 0, 0);
+ weatherData.setMeasurements(1, 1, 1);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: 0.0 0.0 0.0
+StatisticsDisplay.update: 0.0 0.0 0.0
+CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: 1.0 1.0 1.0
+StatisticsDisplay.update: 1.0 1.0 1.0
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Observer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Observer.html)
+- [java.util.EventListener](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/EventListener.html)
+- [javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener](http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/servlet/http/HttpSessionBindingListener.html)
+- [RxJava](https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxJava)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+以下是一个规则检验器实现,具有 and 和 or 规则,通过规则可以构建一颗解析树,用来检验一个文本是否满足解析树定义的规则。
+
+例如一颗解析树为 D And (A Or (B C)),文本 "D A" 满足该解析树定义的规则。
+
+这里的 Context 指的是 String。
+
+```java
+public abstract class Expression {
+ public abstract boolean interpret(String str);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class TerminalExpression extends Expression {
+
+ private String literal = null;
+
+ public TerminalExpression(String str) {
+ literal = str;
+ }
+
+ public boolean interpret(String str) {
+ StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(str);
+ while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
+ String test = st.nextToken();
+ if (test.equals(literal)) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class AndExpression extends Expression {
+
+ private Expression expression1 = null;
+ private Expression expression2 = null;
+
+ public AndExpression(Expression expression1, Expression expression2) {
+ this.expression1 = expression1;
+ this.expression2 = expression2;
+ }
+
+ public boolean interpret(String str) {
+ return expression1.interpret(str) && expression2.interpret(str);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class OrExpression extends Expression {
+ private Expression expression1 = null;
+ private Expression expression2 = null;
+
+ public OrExpression(Expression expression1, Expression expression2) {
+ this.expression1 = expression1;
+ this.expression2 = expression2;
+ }
+
+ public boolean interpret(String str) {
+ return expression1.interpret(str) || expression2.interpret(str);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ /**
+ * 构建解析树
+ */
+ public static Expression buildInterpreterTree() {
+ // Literal
+ Expression terminal1 = new TerminalExpression("A");
+ Expression terminal2 = new TerminalExpression("B");
+ Expression terminal3 = new TerminalExpression("C");
+ Expression terminal4 = new TerminalExpression("D");
+ // B C
+ Expression alternation1 = new OrExpression(terminal2, terminal3);
+ // A Or (B C)
+ Expression alternation2 = new OrExpression(terminal1, alternation1);
+ // D And (A Or (B C))
+ return new AndExpression(terminal4, alternation2);
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Expression define = buildInterpreterTree();
+ String context1 = "D A";
+ String context2 = "A B";
+ System.out.println(define.interpret(context1));
+ System.out.println(define.interpret(context2));
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+true
+false
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Pattern](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/regex/Pattern.html)
+- [java.text.Normalizer](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/text/Normalizer.html)
+- All subclasses of [java.text.Format](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/text/Format.html)
+- [javax.el.ELResolver](http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/el/ELResolver.html)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Element {
+ void accept(Visitor visitor);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+class CustomerGroup {
+
+ private List customers = new ArrayList<>();
+
+ void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ for (Customer customer : customers) {
+ customer.accept(visitor);
+ }
+ }
+
+ void addCustomer(Customer customer) {
+ customers.add(customer);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Customer implements Element {
+
+ private String name;
+ private List orders = new ArrayList<>();
+
+ Customer(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ void addOrder(Order order) {
+ orders.add(order);
+ }
+
+ public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ visitor.visit(this);
+ for (Order order : orders) {
+ order.accept(visitor);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Order implements Element {
+
+ private String name;
+ private List- items = new ArrayList();
+
+ Order(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ Order(String name, String itemName) {
+ this.name = name;
+ this.addItem(new Item(itemName));
+ }
+
+ String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ void addItem(Item item) {
+ items.add(item);
+ }
+
+ public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ visitor.visit(this);
+
+ for (Item item : items) {
+ item.accept(visitor);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Item implements Element {
+
+ private String name;
+
+ Item(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
+ visitor.visit(this);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Visitor {
+ void visit(Customer customer);
+
+ void visit(Order order);
+
+ void visit(Item item);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class GeneralReport implements Visitor {
+
+ private int customersNo;
+ private int ordersNo;
+ private int itemsNo;
+
+ public void visit(Customer customer) {
+ System.out.println(customer.getName());
+ customersNo++;
+ }
+
+ public void visit(Order order) {
+ System.out.println(order.getName());
+ ordersNo++;
+ }
+
+ public void visit(Item item) {
+ System.out.println(item.getName());
+ itemsNo++;
+ }
+
+ public void displayResults() {
+ System.out.println("Number of customers: " + customersNo);
+ System.out.println("Number of orders: " + ordersNo);
+ System.out.println("Number of items: " + itemsNo);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Customer customer1 = new Customer("customer1");
+ customer1.addOrder(new Order("order1", "item1"));
+ customer1.addOrder(new Order("order2", "item1"));
+ customer1.addOrder(new Order("order3", "item1"));
+
+ Order order = new Order("order_a");
+ order.addItem(new Item("item_a1"));
+ order.addItem(new Item("item_a2"));
+ order.addItem(new Item("item_a3"));
+ Customer customer2 = new Customer("customer2");
+ customer2.addOrder(order);
+
+ CustomerGroup customers = new CustomerGroup();
+ customers.addCustomer(customer1);
+ customers.addCustomer(customer2);
+
+ GeneralReport visitor = new GeneralReport();
+ customers.accept(visitor);
+ visitor.displayResults();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+customer1
+order1
+item1
+order2
+item1
+order3
+item1
+customer2
+order_a
+item_a1
+item_a2
+item_a3
+Number of customers: 2
+Number of orders: 4
+Number of items: 6
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- javax.lang.model.element.Element and javax.lang.model.element.ElementVisitor
+- javax.lang.model.type.TypeMirror and javax.lang.model.type.TypeVisitor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+


+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public abstract class Handler {
+
+ protected Handler successor;
+
+
+ public Handler(Handler successor) {
+ this.successor = successor;
+ }
+
+
+ protected abstract void handleRequest(Request request);
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteHandler1 extends Handler {
+
+ public ConcreteHandler1(Handler successor) {
+ super(successor);
+ }
+
+
+ @Override
+ protected void handleRequest(Request request) {
+ if (request.getType() == RequestType.TYPE1) {
+ System.out.println(request.getName() + " is handle by ConcreteHandler1");
+ return;
+ }
+ if (successor != null) {
+ successor.handleRequest(request);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteHandler2 extends Handler {
+
+ public ConcreteHandler2(Handler successor) {
+ super(successor);
+ }
+
+
+ @Override
+ protected void handleRequest(Request request) {
+ if (request.getType() == RequestType.TYPE2) {
+ System.out.println(request.getName() + " is handle by ConcreteHandler2");
+ return;
+ }
+ if (successor != null) {
+ successor.handleRequest(request);
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Request {
+
+ private RequestType type;
+ private String name;
+
+
+ public Request(RequestType type, String name) {
+ this.type = type;
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+
+ public RequestType getType() {
+ return type;
+ }
+
+
+ public String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+```java
+public enum RequestType {
+ TYPE1, TYPE2
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+
+ Handler handler1 = new ConcreteHandler1(null);
+ Handler handler2 = new ConcreteHandler2(handler1);
+
+ Request request1 = new Request(RequestType.TYPE1, "request1");
+ handler2.handleRequest(request1);
+
+ Request request2 = new Request(RequestType.TYPE2, "request2");
+ handler2.handleRequest(request2);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```html
+request1 is handle by ConcreteHandler1
+request2 is handle by ConcreteHandler2
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.logging.Logger#log()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/logging/Logger.html#log%28java.util.logging.Level,%20java.lang.String%29)
+- [Apache Commons Chain](https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-chain/index.html)
+- [javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter()](http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/servlet/Filter.html#doFilter-javax.servlet.ServletRequest-javax.servlet.ServletResponse-javax.servlet.FilterChain-)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+### Implementation
+
+```java
+public interface Aggregate {
+ Iterator createIterator();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteAggregate implements Aggregate {
+
+ private Integer[] items;
+
+ public ConcreteAggregate() {
+ items = new Integer[10];
+ for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
+ items[i] = i;
+ }
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public Iterator createIterator() {
+ return new ConcreteIterator(items);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Iterator- {
+
+ Item next();
+
+ boolean hasNext();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class ConcreteIterator
- implements Iterator {
+
+ private Item[] items;
+ private int position = 0;
+
+ public ConcreteIterator(Item[] items) {
+ this.items = items;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public Object next() {
+ return items[position++];
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public boolean hasNext() {
+ return position < items.length;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Aggregate aggregate = new ConcreteAggregate();
+ Iterator iterator = aggregate.createIterator();
+ while (iterator.hasNext()) {
+ System.out.println(iterator.next());
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Iterator](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Iterator.html)
+- [java.util.Enumeration](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Enumeration.html)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/notes/设计模式 - 适配器.md b/notes/设计模式 - 适配器.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..102ff5f0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/notes/设计模式 - 适配器.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+## 1. 适配器(Adapter)
+
+### Intent
+
+把一个类接口转换成另一个用户需要的接口。
+
+
+
+### Class Diagram
+
+
+
+### Implementation
+
+鸭子(Duck)和火鸡(Turkey)拥有不同的叫声,Duck 的叫声调用 quack() 方法,而 Turkey 调用 gobble() 方法。
+
+要求将 Turkey 的 gobble() 方法适配成 Duck 的 quack() 方法,从而让火鸡冒充鸭子!
+
+```java
+public interface Duck {
+ void quack();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public interface Turkey {
+ void gobble();
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class WildTurkey implements Turkey {
+ @Override
+ public void gobble() {
+ System.out.println("gobble!");
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class TurkeyAdapter implements Duck {
+ Turkey turkey;
+
+ public TurkeyAdapter(Turkey turkey) {
+ this.turkey = turkey;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void quack() {
+ turkey.gobble();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```java
+public class Client {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Turkey turkey = new WildTurkey();
+ Duck duck = new TurkeyAdapter(turkey);
+ duck.quack();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### JDK
+
+- [java.util.Arrays#asList()](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Arrays.html#asList%28T...%29)
+- [java.util.Collections#list()](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Collections.html#list-java.util.Enumeration-)
+- [java.util.Collections#enumeration()](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Collections.html#enumeration-java.util.Collection-)
+- [javax.xml.bind.annotation.adapters.XMLAdapter](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/xml/bind/annotation/adapters/XmlAdapter.html#marshal-BoundType-)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+