* [1. 字符串组合](#1-字符串组合)
* [2. 整数组合求和](#2-整数组合求和)
* [3. 数组中重复的数字](#3-数组中重复的数字)
* [4. 二维数组中的查找](#4-二维数组中的查找)
* [5. 替换空格](#5-替换空格)
* [6. 从尾到头打印链表](#6-从尾到头打印链表)
* [7. 重建二叉树](#7-重建二叉树)
* [8. 二叉树的下一个结点](#8-二叉树的下一个结点)
* [9. 用两个栈实现队列](#9-用两个栈实现队列)
* [10.1 斐波那契数列](#101-斐波那契数列)
* [10.2 跳台阶](#102-跳台阶)
* [10.3 矩形覆盖](#103-矩形覆盖)
* [10.4 变态跳台阶](#104-变态跳台阶)
* [11. 旋转数组的最小数字](#11-旋转数组的最小数字)
* [12. 矩阵中的路径](#12-矩阵中的路径)
* [13. 机器人的运动范围](#13-机器人的运动范围)
* [14. 剪绳子](#14-剪绳子)
* [15. 二进制中 1 的个数](#15-二进制中-1-的个数)
* [16. 数值的整数次方](#16-数值的整数次方)
* [参考文献](#参考文献)
# 1. 字符串组合
## 题目描述
给定三种类型的小球P、Q、R,每种小球的数量分别为np、nq、nr个。现在想讲这些小球排成一条直线,但是不允许相同类型的小球相邻,问有多少种排序方法。
如若np=2,nq=1,nr=1则共有6种排列方式:PQRP、QPRP、PRQP、PRPQ、RPQP以及PQPR。如果无法组合出合适的结果,则输出0.
### 输入
```code
一行以空格相隔的三个数,分别表示为np、nq、nr。
```
### 输出
```code
排列方法的数量。
```
### 样例输入
```code
2 1 1
```
### 样例输出
```code
6
```
## 解题思路
本题采用一种比较直接的方式进行解题,分为如下步骤:
1. 求解给定P、Q、R个数的时候的全排列,提供`Python`提供的`itertools.permutations`来实现,此时肯定有很多重复。
2. 去掉重复的情况,通过`Python`提供的`set`来实现。
3. 通过遍历找出相邻元素重复的串。
4. 求两个集合的差集,即为答案。
```python
import itertools
np, nq, nr = [int(k) for k in raw_input().split(" ")]
count = 0
result = []
for i in itertools.permutations("P"*np + "Q"*nq + "R"*nr,np + nq + nr):
result.append(''.join(i))
result_same = []
for element in list(set(result)):
for j in range(1, len(element)):
if element[j-1] == element[j]:
result_same.append(element)
ret_list = list(set(result)^set(result_same))
print len(ret_list)
```
# 2. 整数组合求和
## 题目描述
小米之家是成人糖果店。里面有很多便宜,好用,好玩的产品。中秋节到了,小米之家想给米粉准备一些固定金额大礼包。对于给定的一个金额,需要判断能不能用
不同种产品(一种产品在礼包最多出现一次)组合出来这个金额。聪明的你来帮帮米家的小伙伴吧。
### 输入
```code
输入N(N是正整数, N < = 200)
输入N个价格p(正整数, p <= 10000)用单空格分割
输入金额M(M是正整数,M <= 100000)
```
### 输出
```code
能组合出来输出1
否则输出0
```
### 样例输入
```code
6
99 199 1999 10000 39 1499
10238
```
### 样例输出
```code
1
```
## 解题思路
本题采用一种比较直接的方式进行解题,分为如下步骤:
1. 对输入np进行排序,方便后面快速结束。
2. 求解给定np时候的0~n个组合的和,提供`Python`提供的`itertools.permutations`来实现。
3. 如果较小的数相加已经大于目标,可以提前跳出本次循环。
```python
import itertools
n = int(raw_input())
np = [int(k) for k in raw_input().split(" ")]
np.sort()
sum_np = int(raw_input())
flag = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in itertools.permutations(np, i):
if sum(j) > sum_np:
continue;
if sum(j) == sum_np:
flag = 1;
break;
print flag
```
# 3. 数组中重复的数字
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/623a5ac0ea5b4e5f95552655361ae0a8?tpId=13&tqId=11203&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
在一个长度为 n 的数组里的所有数字都在 0 到 n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的,也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。例如,如果输入长度为 7 的数组 {2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字 2。
要求复杂度为 O(N) + O(1),也就是时间复杂度 O(N),空间复杂度 O(1)。因此不能使用排序的方法,也不能使用额外的标记数组。牛客网讨论区这一题的首票答案使用 nums[i] + length 来将元素标记,这么做会有加法溢出问题。
## 解题思路
这种数组元素在 [0, n-1] 范围内的问题,可以将值为 i 的元素放到第 i 个位置上。
以 (2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5) 为例:
```text-html-basic
position-0 : (2,3,1,0,2,5) // 2 <-> 1
(1,3,2,0,2,5) // 1 <-> 3
(3,1,2,0,2,5) // 3 <-> 0
(0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-1 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-2 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-3 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-4 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // nums[i] == nums[nums[i]], exit
```
遍历到位置 4 时,该位置上的数为 2,但是第 2 个位置上已经有一个 2 的值了,因此可以知道 2 重复。
```java
public boolean duplicate(int[] nums, int length, int[] duplication) {
if (nums == null || length <= 0)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
while (nums[i] != i) {
if (nums[i] == nums[nums[i]]) {
duplication[0] = nums[i];
return true;
}
swap(nums, i, nums[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int t = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = t;
}
```
```python
nums = [int(k) for k in raw_input().split(" ")]
print nums
def duplicate(nums):
if len(nums) <= 0:
return -1, False
for i in range(len(nums)):
while nums[i] != i:
if nums[i] == nums[nums[i]]:
return nums[i], True
t = nums[i]
nums[i] = nums[nums[i]]
nums[nums[i]] = t
# nums[i], nums[nums[i]] = nums[nums[i]], nums[i]
return -1, False
print duplicate(nums)
```
# 4. 二维数组中的查找
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/abc3fe2ce8e146608e868a70efebf62e?tpId=13&tqId=11154&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
```html
Consider the following matrix:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
Given target = 5, return true.
Given target = 20, return false.
```
## 解题思路
从右上角开始查找。矩阵中的一个数,它左边的数都比它小,下边的数都比它大。因此,从右上角开始查找,就可以根据 target 和当前元素的大小关系来缩小查找区间。
复杂度:O(M + N) + O(1)
当前元素的查找区间为左下角的所有元素,例如元素 12 的查找区间如下:

```java
public boolean Find(int target, int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
return false;
int rows = matrix.length, cols = matrix[0].length;
int r = 0, c = cols - 1; // 从右上角开始
while (r <= rows - 1 && c >= 0) {
if (target == matrix[r][c])
return true;
else if (target > matrix[r][c])
r++;
else
c--;
}
return false;
}
```
```python
target = int(input())
# nums = [[1, 4, 7, 11, 15], [2, 5, 8, 12, 19], [3, 6, 9, 16, 22], [10, 13, 14, 17, 24], [18, 21, 23, 26, 30]]
nums = eval(input())
def find(target, matrix):
if len(matrix) == 0 or len(matrix[0]) == 0:
return False
rows, cols = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
r, c = 0, cols - 1
while r <= rows - 1 and c >= 0:
if target == matrix[r][c]:
return True
elif target > matrix[r][c]:
r += 1
else:
c -= 1
return False
print (find(target, nums))
```
# 5. 替换空格
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/4060ac7e3e404ad1a894ef3e17650423?tpId=13&tqId=11155&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
将一个字符串中的空格替换成 "%20"。
```text
Input:
"We Are Happy"
Output:
"We%20Are%20Happy"
```
## 解题思路
在字符串尾部填充任意字符,使得字符串的长度等于替换之后的长度。因为一个空格要替换成三个字符(%20),因此当遍历到一个空格时,需要在尾部填充两个任意字符。
令 P1 指向字符串原来的末尾位置,P2 指向字符串现在的末尾位置。P1 和 P2从后向前遍历,当 P1 遍历到一个空格时,就需要令 P2 指向的位置依次填充 02%(注意是逆序的),否则就填充上 P1 指向字符的值。
从后向前遍是为了在改变 P2 所指向的内容时,不会影响到 P1 遍历原来字符串的内容。
```java
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
int P1 = str.length() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < P1 + 1; i++)
if (str.charAt(i) == ' ')
str.append(" ");
int P2 = str.length() - 1;
while (P1 >= 0 && P2 > P1) {
char c = str.charAt(P1--);
if (c == ' ') {
str.setCharAt(P2--, '0');
str.setCharAt(P2--, '2');
str.setCharAt(P2--, '%');
} else {
str.setCharAt(P2--, c);
}
}
return str.toString();
}
```
```python
target = input()
print (target.replace(" ", "%20"))
```
# 6. 从尾到头打印链表
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d0267f7f55b3412ba93bd35cfa8e8035?tpId=13&tqId=11156&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
输入链表的第一个节点,从尾到头反过来打印出每个结点的值。

## 解题思路
### 使用栈
```java
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
while (listNode != null) {
stack.add(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty())
ret.add(stack.pop());
return ret;
}
```
### 使用递归
```java
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (listNode != null) {
ret.addAll(printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next));
ret.add(listNode.val);
}
return ret;
}
```
### 使用头插法
利用链表头插法为逆序的特点。
头结点和第一个节点的区别:
- 头结点是在头插法中使用的一个额外节点,这个节点不存储值;
- 第一个节点就是链表的第一个真正存储值的节点。
```java
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
// 头插法构建逆序链表
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
while (listNode != null) {
ListNode memo = listNode.next;
listNode.next = head.next;
head.next = listNode;
listNode = memo;
}
// 构建 ArrayList
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
head = head.next;
while (head != null) {
ret.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
return ret;
}
```
### 使用 Collections.reverse()
```java
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
while (listNode != null) {
ret.add(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
Collections.reverse(ret);
return ret;
}
```
```python
def printListFromTailToHead(listNode):
# write code here
l = list()
while listNode:
l.append(listNode.val)
listNode = listNode.next
l.reverse()
return l
```
# 7. 重建二叉树
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8a19cbe657394eeaac2f6ea9b0f6fcf6?tpId=13&tqId=11157&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
根据二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
```html
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
```

## 解题思路
前序遍历的第一个值为根节点的值,使用这个值将中序遍历结果分成两部分,左部分为树的左子树中序遍历结果,右部分为树的右子树中序遍历的结果。
```java
// 缓存中序遍历数组每个值对应的索引
private Map indexForInOrders = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre, int[] in) {
for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++)
indexForInOrders.put(in[i], i);
return reConstructBinaryTree(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, 0);
}
private TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre, int preL, int preR, int inL) {
if (preL > preR)
return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[preL]);
int inIndex = indexForInOrders.get(root.val);
int leftTreeSize = inIndex - inL;
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, preL + 1, preL + leftTreeSize, inL);
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, preL + leftTreeSize + 1, preR, inL + leftTreeSize + 1);
return root;
}
```
```python
# 返回构造的TreeNode根节点
def reConstructBinaryTree(self, pre, tin):
# write code here
if not pre or not tin:
return None
root = TreeNode(pre.pop(0))
index = tin.index(root.val)
root.left = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre, tin[:index])
root.right = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre, tin[index + 1:])
return root
```
# 8. 二叉树的下一个结点
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9023a0c988684a53960365b889ceaf5e?tpId=13&tqId=11210&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
```java
public class TreeLinkNode {
int val;
TreeLinkNode left = null;
TreeLinkNode right = null;
TreeLinkNode next = null;
TreeLinkNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
```
## 解题思路
① 如果一个节点的右子树不为空,那么该节点的下一个节点是右子树的最左节点;

② 否则,向上找第一个左链接指向的树包含该节点的祖先节点。

```java
public TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode pNode) {
if (pNode.right != null) {
TreeLinkNode node = pNode.right;
while (node.left != null)
node = node.left;
return node;
} else {
while (pNode.next != null) {
TreeLinkNode parent = pNode.next;
if (parent.left == pNode)
return parent;
pNode = pNode.next;
}
}
return null;
}
```
```python
def GetNext(self, pNode):
# write code here
# pNode is None
if not pNode:
return pNode
if pNode.right:
node = pNode.right
while node.left:
node = node.left
return node
else:
while pNode.next:
parent = pNode.next
if parent.left == pNode:
return parent
pNode = pNode.next
# pNode not have the next node
return None
```
# 9. 用两个栈实现队列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/54275ddae22f475981afa2244dd448c6?tpId=13&tqId=11158&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的 Push 和 Pop 操作。
## 解题思路
in 栈用来处理入栈(push)操作,out 栈用来处理出栈(pop)操作。一个元素进入 in 栈之后,出栈的顺序被反转。当元素要出栈时,需要先进入 out 栈,此时元素出栈顺序再一次被反转,因此出栈顺序就和最开始入栈顺序是相同的,先进入的元素先退出,这就是队列的顺序。

```java
Stack in = new Stack();
Stack out = new Stack();
public void push(int node) {
in.push(node);
}
public int pop() throws Exception {
if (out.isEmpty())
while (!in.isEmpty())
out.push(in.pop());
if (out.isEmpty())
throw new Exception("queue is empty");
return out.pop();
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.stack1 = []
self.stack2 = []
def push(self, node):
# write code here
self.stack1.append(node)
def pop(self):
# return xx
if self.stack2 == []:
while self.stack1:
self.stack2.append(self.stack1.pop())
return self.stack2.pop()
return self.stack2.pop()
```
# 10.1 斐波那契数列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/c6c7742f5ba7442aada113136ddea0c3?tpId=13&tqId=11160&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
求斐波那契数列的第 n 项,n <= 39。
=\left\{\begin{array}{rcl}0&&{n=0}\\1&&{n=1}\\f(n-1)+f(n-2)&&{n>1}\end{array}\right.)
## 解题思路
如果使用递归求解,会重复计算一些子问题。例如,计算 f(10) 需要计算 f(9) 和 f(8),计算 f(9) 需要计算 f(8) 和 f(7),可以看到 f(8) 被重复计算了。
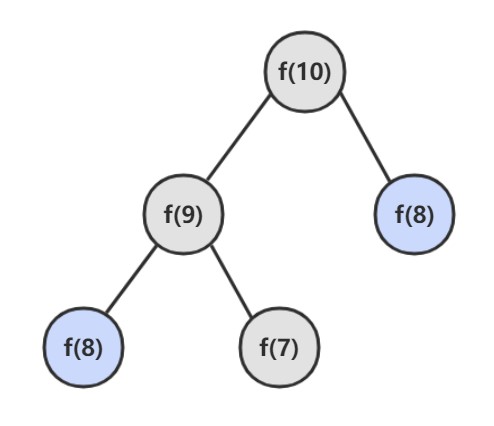
递归是将一个问题划分成多个子问题求解,动态规划也是如此,但是动态规划会把子问题的解缓存起来,从而避免重复求解子问题。
```java
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
int[] fib = new int[n + 1];
fib[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
return fib[n];
}
```
考虑到第 i 项只与第 i-1 和第 i-2 项有关,因此只需要存储前两项的值就能求解第 i 项,从而将空间复杂度由 O(N) 降低为 O(1)。
```java
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
int pre2 = 0, pre1 = 1;
int fib = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
fib = pre2 + pre1;
pre2 = pre1;
pre1 = fib;
}
return fib;
}
```
由于待求解的 n 小于 40,因此可以将前 40 项的结果先进行计算,之后就能以 O(1) 时间复杂度得到第 n 项的值了。
```java
public class Solution {
private int[] fib = new int[40];
public Solution() {
fib[1] = 1;
fib[2] = 2;
for (int i = 2; i < fib.length; i++)
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
}
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
return fib[n];
}
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.fib = [0,1]
for i in range(2,40):
self.fib.append(self.fib[i-1]+self.fib[i-2])
def Fibonacci(self, n):
# write code here
return self.fib[n]
```
# 10.2 跳台阶
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8c82a5b80378478f9484d87d1c5f12a4?tpId=13&tqId=11161&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上 1 级台阶,也可以跳上 2 级。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
## 解题思路
```java
public int JumpFloor(int n) {
if (n <= 2)
return n;
int pre2 = 1, pre1 = 2;
int result = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
result = pre2 + pre1;
pre2 = pre1;
pre1 = result;
}
return result;
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def jumpFloor(self, number):
# write code here
if number == 0:
return number
pre1, pre2 = 1, 1
#result = 0
for i in range(number):
pre1, pre2 = pre2, pre1+pre2
return pre1
```
# 10.3 矩形覆盖
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/72a5a919508a4251859fb2cfb987a0e6?tpId=13&tqId=11163&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
我们可以用 2\*1 的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用 n 个 2\*1 的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个 2\*n 的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
## 解题思路
```java
public int RectCover(int n) {
if (n <= 2)
return n;
int pre2 = 1, pre1 = 2;
int result = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
result = pre2 + pre1;
pre2 = pre1;
pre1 = result;
}
return result;
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def rectCover(self, number):
# write code here
if number == 0:
return number
pre1, pre2 = 1, 1
#result = 0
for i in range(number):
pre1, pre2 = pre2, pre1+pre2
return pre1
```
# 10.4 变态跳台阶
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/22243d016f6b47f2a6928b4313c85387?tpId=13&tqId=11162&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上 1 级台阶,也可以跳上 2 级... 它也可以跳上 n 级。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
## 解题思路
```java
public int JumpFloorII(int target) {
int[] dp = new int[target];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < target; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
dp[i] += dp[j];
return dp[target - 1];
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def jumpFloorII(self, number):
# write code here
if number <= 0:
return 0
return pow(2, number-1)
```
# 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9f3231a991af4f55b95579b44b7a01ba?tpId=13&tqId=11159&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个非递减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
例如数组 {3, 4, 5, 1, 2} 为 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为 1。
## 解题思路
在一个有序数组中查找一个元素可以用二分查找,二分查找也称为折半查找,每次都能将查找区间减半,这种折半特性的算法时间复杂度都为 O(logN)。
本题可以修改二分查找算法进行求解:
- 当 nums[m] <= nums[h] 的情况下,说明解在 [l, m] 之间,此时令 h = m;
- 否则解在 [m + 1, h] 之间,令 l = m + 1。
```java
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (nums[m] <= nums[h])
h = m;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return nums[l];
}
```
如果数组元素允许重复的话,那么就会出现一个特殊的情况:nums[l] == nums[m] == nums[h],那么此时无法确定解在哪个区间,需要切换到顺序查找。例如对于数组 {1,1,1,0,1},l、m 和 h 指向的数都为 1,此时无法知道最小数字 0 在哪个区间。
```java
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (nums[l] == nums[m] && nums[m] == nums[h])
return minNumber(nums, l, h);
else if (nums[m] <= nums[h])
h = m;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return nums[l];
}
private int minNumber(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
for (int i = l; i < h; i++)
if (nums[i] > nums[i + 1])
return nums[i + 1];
return nums[l];
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def minNumberInRotateArray(self, rotateArray):
# write code here
if len(rotateArray) == 0:
return 0
return min(rotateArray)
```
# 12. 矩阵中的路径
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/c61c6999eecb4b8f88a98f66b273a3cc?tpId=13&tqId=11218&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则该路径不能再进入该格子。
例如下面的矩阵包含了一条 bfce 路径。

## 解题思路
```java
private final static int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
private int rows;
private int cols;
public boolean hasPath(char[] array, int rows, int cols, char[] str) {
if (rows == 0 || cols == 0)
return false;
this.rows = rows;
this.cols = cols;
boolean[][] marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
char[][] matrix = buildMatrix(array);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
if (backtracking(matrix, str, marked, 0, i, j))
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean backtracking(char[][] matrix, char[] str, boolean[][] marked, int pathLen, int r, int c) {
if (pathLen == str.length)
return true;
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols || matrix[r][c] != str[pathLen] || marked[r][c])
return false;
marked[r][c] = true;
for (int[] n : next)
if (backtracking(matrix, str, marked, pathLen + 1, r + n[0], c + n[1]))
return true;
marked[r][c] = false;
return false;
}
private char[][] buildMatrix(char[] array) {
char[][] matrix = new char[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0, idx = 0; i < rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
matrix[i][j] = array[idx++];
return matrix;
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def hasPath(self, matrix, rows, cols, path):
# write code here
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if matrix[i*cols+j] == path[0]:
if self.find(list(matrix),rows,cols,path[1:],i,j):
return True
return False
def find(self,matrix,rows,cols,path,i,j):
if not path:
return True
matrix[i*cols+j]='0'
if j+1=0 and matrix[i*cols+j-1]==path[0]:
return self.find(matrix,rows,cols,path[1:],i,j-1)
elif i+1=0 and matrix[(i-1)*cols+j]==path[0]:
return self.find(matrix,rows,cols,path[1:],i-1,j)
else:
return False
def buildMatrix(self, matrix):
array = [[0]*self.cols for i in range(self.rows)]
for i in range(self.rows):
idx = 0
for j in range(self.cols):
array[i][j] = matrix[idx]
idx += 1
return array
```
# 13. 机器人的运动范围
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6e5207314b5241fb83f2329e89fdecc8?tpId=13&tqId=11219&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
地上有一个 m 行和 n 列的方格。一个机器人从坐标 (0, 0) 的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左右上下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。
例如,当 k 为 18 时,机器人能够进入方格 (35,37),因为 3+5+3+7=18。但是,它不能进入方格 (35,37),因为 3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
## 解题思路
```java
private static final int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
private int cnt = 0;
private int rows;
private int cols;
private int threshold;
private int[][] digitSum;
public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {
this.rows = rows;
this.cols = cols;
this.threshold = threshold;
initDigitSum();
boolean[][] marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
dfs(marked, 0, 0);
return cnt;
}
private void dfs(boolean[][] marked, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols || marked[r][c])
return;
marked[r][c] = true;
if (this.digitSum[r][c] > this.threshold)
return;
cnt++;
for (int[] n : next)
dfs(marked, r + n[0], c + n[1]);
}
private void initDigitSum() {
int[] digitSumOne = new int[Math.max(rows, cols)];
for (int i = 0; i < digitSumOne.length; i++) {
int n = i;
while (n > 0) {
digitSumOne[i] += n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
}
this.digitSum = new int[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0; i < this.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < this.cols; j++)
this.digitSum[i][j] = digitSumOne[i] + digitSumOne[j];
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.acc = 0
def movingCount(self, threshold, rows, cols):
# write code here
self.threshold = threshold
self.rows = rows
self.cols = cols
self.board = [[0 for _ in range(cols)] for _ in range(rows)]
self.traverse(0,0)
return self.acc
def block(self, r, c):
s = sum(map(int,str(r)+str(c)))
return s>self.threshold
def traverse(self, r, c):
if not (0<=r= 5 时,3(n - 3) - 2(n - 2) = n - 5 >= 0。因此把长度大于 5 的绳子切成两段,令其中一段长度为 3 可以使得两段的乘积最大。
```java
public int integerBreak(int n) {
if (n < 2)
return 0;
if (n == 2)
return 1;
if (n == 3)
return 2;
int timesOf3 = n / 3;
if (n - timesOf3 * 3 == 1)
timesOf3--;
int timesOf2 = (n - timesOf3 * 3) / 2;
return (int) (Math.pow(3, timesOf3)) * (int) (Math.pow(2, timesOf2));
}
```
```python
def integerBreak(n):
if n < 2:
return 0
if n == 2:
return 1
if n == 3:
return 2
timesOf3 = n // 3
if n - timesOf3 * 3 == 1:
timesOf3 -= 1
timesOf2 = (n - timesOf3 * 3) // 2
return pow(3, timesOf3) * pow(2, timesOf2)
```
# 15. 二进制中 1 的个数
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8ee967e43c2c4ec193b040ea7fbb10b8?tpId=13&tqId=11164&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中 1 的个数。
### n&(n-1)
该位运算去除 n 的位级表示中最低的那一位。
```
n : 10110100
n-1 : 10110011
n&(n-1) : 10110000
```
时间复杂度:O(M),其中 M 表示 1 的个数。
```java
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
while (n != 0) {
cnt++;
n &= (n - 1);
}
return cnt;
}
```
### Integer.bitCount()
```java
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
return Integer.bitCount(n);
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def NumberOf1(self, n):
# write code here
if n<0:
n=n&0xFFFFFFFF #把负号去掉,如果负号在后面会陷入死循环
return bin(n).count('1')
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def NumberOf1(self, n):
# write code here
return sum([(n>>i & 1) for i in range(0,32)])
```
# 16. 数值的整数次方
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/1a834e5e3e1a4b7ba251417554e07c00?tpId=13&tqId=11165&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
## 题目描述
给定一个 double 类型的浮点数 base 和 int 类型的整数 exponent,求 base 的 exponent 次方。
## 解题思路
下面的讨论中 x 代表 base,n 代表 exponent。
因为 (x\*x)n/2 可以通过递归求解,并且每次递归 n 都减小一半,因此整个算法的时间复杂度为 O(logN)。
```java
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if (exponent == 0)
return 1;
if (exponent == 1)
return base;
boolean isNegative = false;
if (exponent < 0) {
exponent = -exponent;
isNegative = true;
}
double pow = Power(base * base, exponent / 2);
if (exponent % 2 != 0)
pow = pow * base;
return isNegative ? 1 / pow : pow;
}
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Power(self, base, exponent):
# write code here
flag = 0
if base == 0:
return False
if exponent == 0:
return 1
if exponent < 0:
flag = 1
result = 1
for i in range(abs(exponent)):
result *= base
if flag == 1:
result = 1 / result
return result
```
```python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Power(self, base, exponent):
# write code here
return pow(base, exponent)
```
### 动态规划
```java
public int integerBreak(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * (i - j), dp[j] * (i - j)));
return dp[n];
}
```
### 动态规划
```java
public int integerBreak(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * (i - j), dp[j] * (i - j)));
return dp[n];
}
```
# 参考文献
- 何海涛. 剑指 Offer[M]. 电子工业出版社, 2012.








